Find out which foods are rich in vitamin E and check the effects of the nutrient on the body, skin and hair
html[data-range=”xlarge”] figure image img.img-f2ce6efb19fec9ac2925c954f00408616b6n00ey { width: 774px; height: 516px; }HTML[data-range=”large”] figure image img.img-f2ce6efb19fec9ac2925c954f00408616b6n00ey { width: 548px; height: 365px; }HTML[data-range=”small”] figure image img.img-f2ce6efb19fec9ac2925c954f00408616b6n00ey, html[data-range=”medium”] figure image img.img-f2ce6efb19fec9ac2925c954f00408616b6n00ey { width: 564px; height: 376px; }
We know that the Vitamin E It is essential for the body to function properly, but what is it for? Where is it found and what can cause a lack of this vitamin in our body?
What is vitamin E used for?
Also known as tocopherol, vitamin E performs an antioxidant function and has anti-inflammatory properties, which help improve the immune system, skin and hair.
Because it is a fat-soluble vitamin, it has an affinity for fat, being stored in adipose tissue and the liver.
What are the benefits
The main benefit of vitamin E is to protect cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. It also prevents cellular aging and helps maintain the health of the immune, cardiac and nervous systems (prevention of neurological diseases).
When vitamin E is combined with other nutrients, such as selenium, it helps repair and rebuild tissue, strengthening hair and nails.
Due to the antioxidant function, which prevents premature aging of skin cells, the vitamin plays a role in reducing wrinkles, expression lines and speeding up healing.
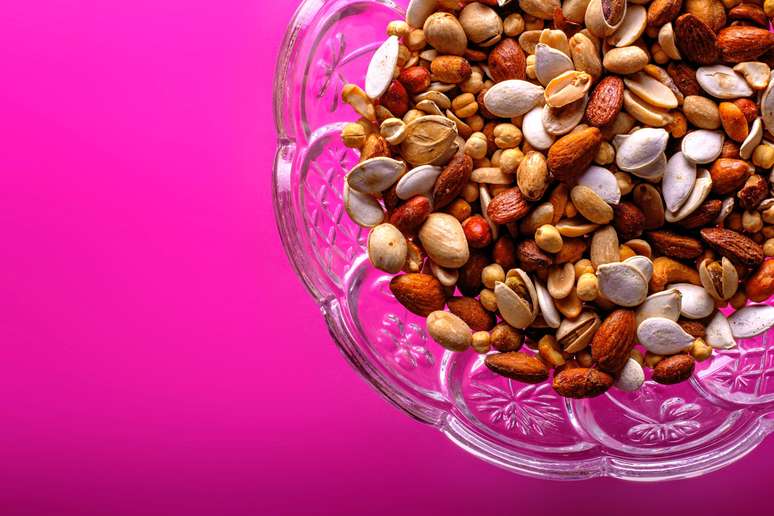
Sources of vitamin E
Since our body is unable to synthesize it, we have to ingest the nutrient through food or supplementation. It is mainly found in vegetable oils and dried fruits.
According to Bruno Guimarães, nutritionist and specialist in exercise physiology at the Catholic University of Brasilia, while most people need to ingest 15 mg of the vitamin a day, there is no ideal dose. “Because this is something very specific, we have to analyze each case to find the best possible therapy.”
Foods
- Corn oil
- Sunflower seeds
- almonds
- Spinach
- Watercress
- Cabbage
- Rocket
- dried tomato
- Olive oil
- Cashew nuts
- wheat bran
- Brazil nuts
- Pistachio
- Black olive
- Avocado
- Hazelnut
- Papaya
- dried apricots
- Asparagus
Supplementation
Guimarães explains that it will be necessary to take vitamin supplements only according to its concentration in the body. “There’s no need to supplement if your levels are adequate, making use of food sources. However, if you do need supplementation, you can use it daily,” he adds.
In addition to being indicated in cases of low concentration in the body, vitamin E supplementation can also be recommended by the doctor in the following situations:
- People with fat malabsorption: patients after bariatric surgery, with irritable bowel syndrome or chronic pancreatitis
- Premature infants: to avoid retinopathy and haemolytic anemia
- Patients with high cholesterol: Vitamin improves blood circulation
- People with high blood pressure: Nutrients regulate blood pressure
- Couples with fertility problems
What does a lack of vitamin E do to the body?
The exercise physiology specialist says that when patients are deficient in this nutrient, they can experience the impacts of oxidative stress, such as: fatigue, depressed mood, muscle weakness and impaired reflexes. In severe cases, a lack of the vitamin can lead to neurological disease and vision problems.
Furthermore, when there is an imbalance in the body, i.e. a lot of oxidative stress, a kind of priority distribution of the vitamin reserve is created. Normally, the most central organs end up being prioritized and skin, hair and nails tend to be overlooked in this distribution.
Source: Terra
Ben Stock is a lifestyle journalist and author at Gossipify. He writes about topics such as health, wellness, travel, food and home decor. He provides practical advice and inspiration to improve well-being, keeps readers up to date with latest lifestyle news and trends, known for his engaging writing style, in-depth analysis and unique perspectives.