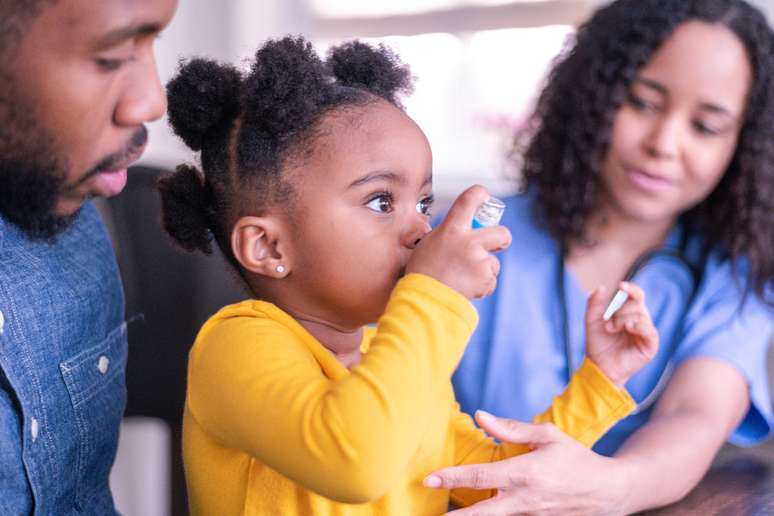
Allergic bronchitis is the most frequent respiratory disorder in the first years of life. Early treatment is recommended.
The World Health Organization (WHO) points out that there are 339 million people with asthma in the world. When you look at the child population, the reality is also worrying. “Asthma is estimated to affect 25% of children under 12 living in large cities,” calculates the doctor José Carlos Perini, president of the Brazilian Association of Allergy and Immunology (ASBAI). It is the most common chronic disease in childhood.occurring in 10-15 percent of children, according to the Pediatric Society of São Paulo (SPSP).
html[data-range=”xlarge”] figure image img.img-23a397e07d02650477109346940e7ec5v983t30y { width: 774px; height: 516px; }HTML[data-range=”large”] figure image img.img-23a397e07d02650477109346940e7ec5v983t30y { width: 548px; height: 365px; }HTML[data-range=”small”] figure image img.img-23a397e07d02650477109346940e7ec5v983t30y, html[data-range=”medium”] figure image img.img-23a397e07d02650477109346940e7ec5v983t30y { width: 564px; height: 376px; }
What is asthma?
Asthma, or allergic bronchitis, is an inflammatory disease that affects the lungs and bronchi. (the tubes that carry air in the body). Importantly, “bronchitis” is a generic term for inflammation of the bronchi, which can be caused by smoking, allergic processes, and primarily viral or bacterial infections, according to the SPSP. Allergic bronchitis or asthmatic bronchitis — the same as asthma — is the most common cause in children and is triggered by allergenic factors.
The disease can be classified in several ways: when it appears from time to time, it is intermittent. When you show up often, persistent. In the latter case, the disease can evolve in a mild, moderate or severe way. Severity is analyzed by the need for therapeutic resources. ” An individual who does not respond to conventional medications will be considered to have severe asthma.“, explains Perini.
Treatment involves the use of bronchodilators, anti-inflammatories and corticosteroids. The severe form of the disease is treated with a combination of these drugs. However there are cases – very serious – in which the patient does not even respond to these heavy combos.
There, one option would be to resort to omalizumab, a drug administered only in hospitals. “It is indicated for very severe cases of asthma, which we cannot control with the usual medicines,” informs pediatric pulmonologist Luiz Vicente Ribeiro, of the Albert Einstein Hospital Israelita, in São Paulo. Omalizumab can be administered in adults and children from 6 years and, at the end of 2019, the incorporation of the drug was approved in the public health network in Brazil.
Asthma symptoms in children
The main symptoms of asthma in children are coughing and wheezing. “The cough is the first to appear and the last to disappear. Then comes the wheezing, the child makes a noise as if it were a kitten”, reports the pediatrician Marta Cristina Duarte, professor at the Maternal-Infant Department of the Faculty of Medicine at the Federal University of Juiz de Fora (UFJF), in Minas Gerais.
If not treated quickly, the child also tends to have shortness of breath. “This happens because the bronchi go into spasm,” says the specialist. In other words, intense inflammation causes the the pipes begin to contractwhich makes it difficult for air to pass through.
It is worth noting that there is no age for these signs to appear. “There are children who start having symptoms with 1 month old and others with 3 years“, exemplifies the pediatrician. In children, asthma also causes irritability, difficulty sleeping and depression. In this case, it is advisable to seek immediate medical attention.
nocturnal asthma
At night, it is common for asthma symptoms worsen in infant and toddler. The situation happens for several reasons. The first is that we are at home, a place where many mites are concentrated. Also, at this time, the temperature tends to drop, which also causes coughing and wheezing.
There is a question that also concerns our body at night: “Cortisol levels are lower, opening the door for asthma to manifest“, says Marta Cristina. Cortisol is a hormone produced by our body, which acts as an anti-inflammatory. Therefore, the more it circulates in the body, the less inflammatory reactions we have. And asthma – for those suffering from the disease – is one of them.
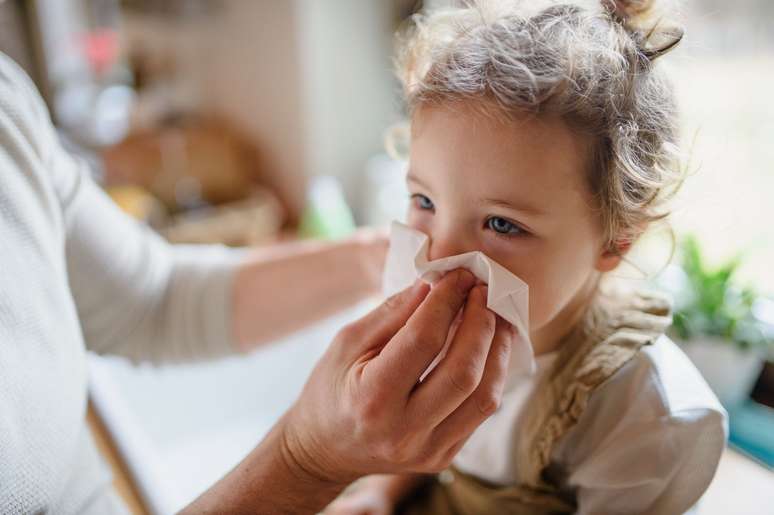

Causes of childhood asthma
Little asthmatics are born with a genetic predisposition to develop the problem. Associated with this, exposure to allergenic factors (such as mites, moulds, cigarette smoke and dust) also opens the door to this inflammatory disease. Therefore, the combination of family history and the child’s environment may be decisive for the onset of asthma.
Disease diagnosis
Identification of asthma is based on the patient’s symptoms and response to treatment. “There is no specific exam for this,” the UFJF professor points out. Diagnosing early in life is also difficult, because many children wheeze up to age 3. Subsequently, the symptom disappears. “In this age group, it is necessary to combine a number of criteria to arrive at the conclusion that it is asthma,” says Luiz Vicente Ribeiro.
The observation is usually made by the pediatrician himself., which is able to cure the disease. However, if the child does not respond to medications and symptoms worsen to the point of interrupting the patient’s or family’s routine, it is advisable to consult a pediatric pulmonologist, a specialist in the field.
Treatment of asthma in children
There is no cure for asthma, but with adequate treatment, the disease tends to disappear, on average, around 10 years of age. “Statistically, 50% of children who become asthmatic before the age of 6 achieve remission of the disease by adolescence,” says José Carlos Perini. Even so, there are instances where the problem persists for life. Therefore, the recommendation is to treat early.
In childhood, the main treatment is inhaled corticosteroids and leukotriene modifiers, which work to prevent inflammation. Older children have the option of using long-acting bronchodilators, the famous firecrackers. “They are called that because they last longer: 8 or even 12 hours,” underlines the Einstein specialist.
All of these drugs are indicated to prevent seizures. During acute conditions, short-acting bronchodilators are recommended., which are also shaped like firecrackers. If the seizure is very intense, your doctor may prescribe corticosteroids by mouth or injection.
Is there any way to prevent asthma in children?
Unfortunately, there is no guarantee that asthma will never occur. “No study has shown that it is possible to prevent children at high risk for the disease from developing it over time,” informs Ribeiro. However, in addition to conventional treatment, some non-pharmacological measures help prevent seizures.
The main one is avoid exposure to allergenic factors that trigger the symptoms. Another important resource for young asthmatics is physical activity – but then it is essential that the disease is under control. “Uncontrolled individuals can have seizure episodes during sports activity”, warns the pediatric pulmonologist.
Source: Terra
Ben Stock is a lifestyle journalist and author at Gossipify. He writes about topics such as health, wellness, travel, food and home decor. He provides practical advice and inspiration to improve well-being, keeps readers up to date with latest lifestyle news and trends, known for his engaging writing style, in-depth analysis and unique perspectives.