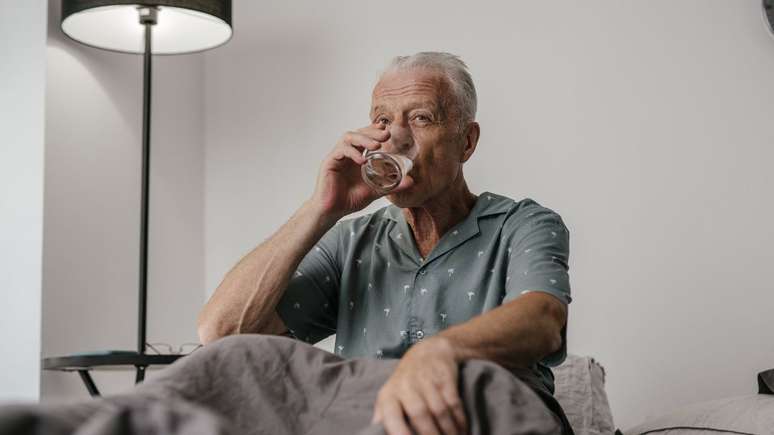
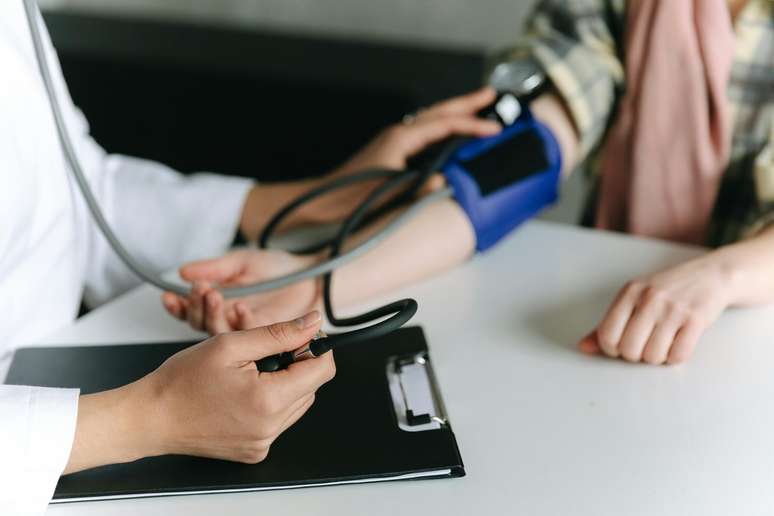
The expert explains the need for elderly people to hydrate after six in the afternoon
How many times have we heard the elderly in our family say that they won’t drink water at night, because they are afraid of having to get up at dawn to urinate and of falling? Despite the decision, the gerontologist Alexander Kalache warns family members to insist on drinking the liquid before going to sleep. Understand:
Danger of stroke
In an interview with TV Brazilthe specialist said that the elderly do not feel thirsty and this is a natural process over time. In addition to this factor, he is also afraid of getting up during sleeping hours. “He lets himself be dominated by the following idea: ‘I won’t drink liquids at night because I have to wake up to pee'”he detailed. On the other hand, this could have a certain consequence.
“If you don’t hydrate at night, your blood can become thicker. And vascular accidents, also known as strokes, generally occur in the morning, because the blood has become thick and can’t circulate.”he explained, stressing that you need to drink water after six in the afternoon.
How many liters of water should seniors drink per day?
According to experts, healthy seniors should drink about two liters of water a day. This is because the recommendation is to consume 30 ml of water per kilogram of body weight. However, the ideal varies depending on each patient’s profile. Therefore an individual evaluation with a healthcare professional is necessary.
Older adults should do vigorous weight training
Another topic that isn’t talked about as much is the importance of older adults doing vigorous weight training. See part of the article below and read it in full.
THE University of Copenhagen she was curious whether strength training, such as bodybuilding and weight lifting, could have long-term effects and minimize the loss of muscle and strength in older adults. To do this, they called 451 healthy seniors to participate in a program that would last a year. They divided them into three groups.
One of them trained under supervision in the gym three times a week, using a load that varied between 70% and 80% of the maximum weight and performing three sets of exercises of six to twelve repetitions. For the second they prescribed moderate exercises, with 50%-60% of the maximum load, using lighter materials, such as elastic bands. The third served as a control group and did not undergo any specific training.
To reach the results, they evaluated the volunteers at the beginning, when they had completed 12 months, after two and four years. By the end, everyone had lost lean mass and strength. However, those who trained more intensely had the same abilities as at the beginning. “This happened because the training significantly increased their strength. So, even with the fall, they managed to maintain what they had”explains the physical education professional, Everton Crivoi do Carmo.
Source: Terra
Ben Stock is a lifestyle journalist and author at Gossipify. He writes about topics such as health, wellness, travel, food and home decor. He provides practical advice and inspiration to improve well-being, keeps readers up to date with latest lifestyle news and trends, known for his engaging writing style, in-depth analysis and unique perspectives.




![Such an excellent sun in advance: Summary of the episode on Monday, August 25, 2025 [SPOILERS] Such an excellent sun in advance: Summary of the episode on Monday, August 25, 2025 [SPOILERS]](https://fr.web.img4.acsta.net/img/d4/f7/d4f7205d1d5c20b03112603176615360.jpg)



