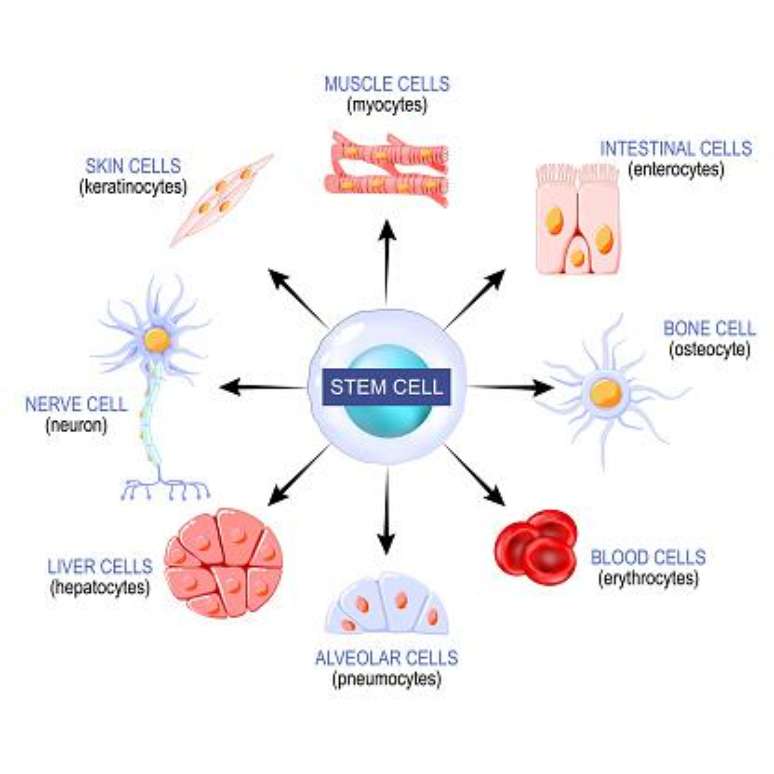
Collaboration between researchers from Germany, Canada, Spain and the United States led to a study that correlates the number of cells in the human body, its dimensions and its functions, indicating a unique balance. When we talk about our most basic units, we may have the mistaken thought that they are all the same, simply distributed in different areas of our body.
But our cells they are very different from each other, whether in size, function or distribution. A neuron, for example, could never be replaced by an epithelial cell, nor could a unit of heart muscle be transplanted into the biceps.
However, in addition to those that make up the human body, we also host other types of organisms, such as bacteria. It is estimated that in total we have at least 38 trillion bacterial cells living friendly inside us.
But even if we know their specifics, we still don’t have a complete mapping of them all. With this in mind, the international collaboration investigated more than 1,500 studies on the topic and pooled data from 1,200 groups of cells.
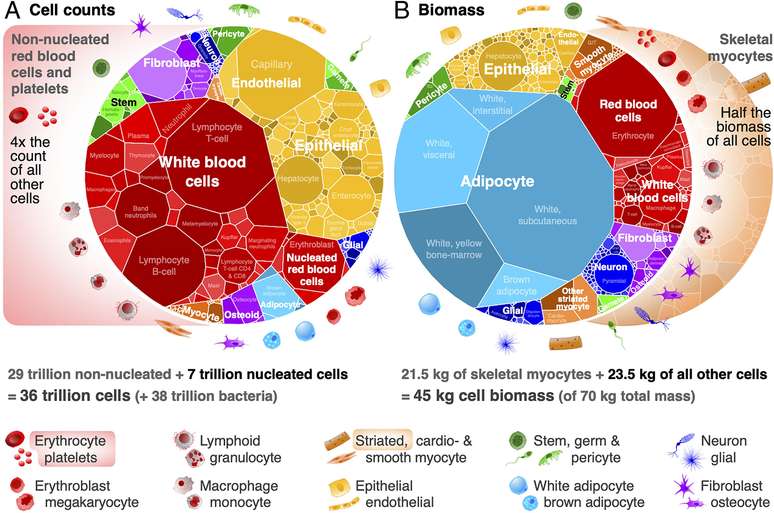
To make the data more accessible, they set up a website with the mapping carried out, divided by regions and types. The group was able to observe some interesting things while analyzing the data. The first is the relationship between sex, weight and quantity.
In a practical example, a man with an average weight of 70 kilograms is estimated to have an average of 36 trillion cells. Women, who weigh 60 kilograms, weigh 28 trillion and 10-year-old children can hold about 17 trillion.
But the real surprise lies in the inverse relationship between size and quantity. The smaller the cells, the greater their number in the body. However, the different cell groups contribute in a balanced way to the formation of body mass.
For researchers, they somehow maintain intelligent regulation with each other, regulating their production and forming a homeostatic balance. It is as if for one large cell there must exist 10 other small cells to balance the scales of existence.
However, not everything is so balanced. In the article’s discussion, the researchers list several challenges in analyzing the data, such as outdated technology and discrepancies between the literature and observational data regarding cell size, shape, and mass.
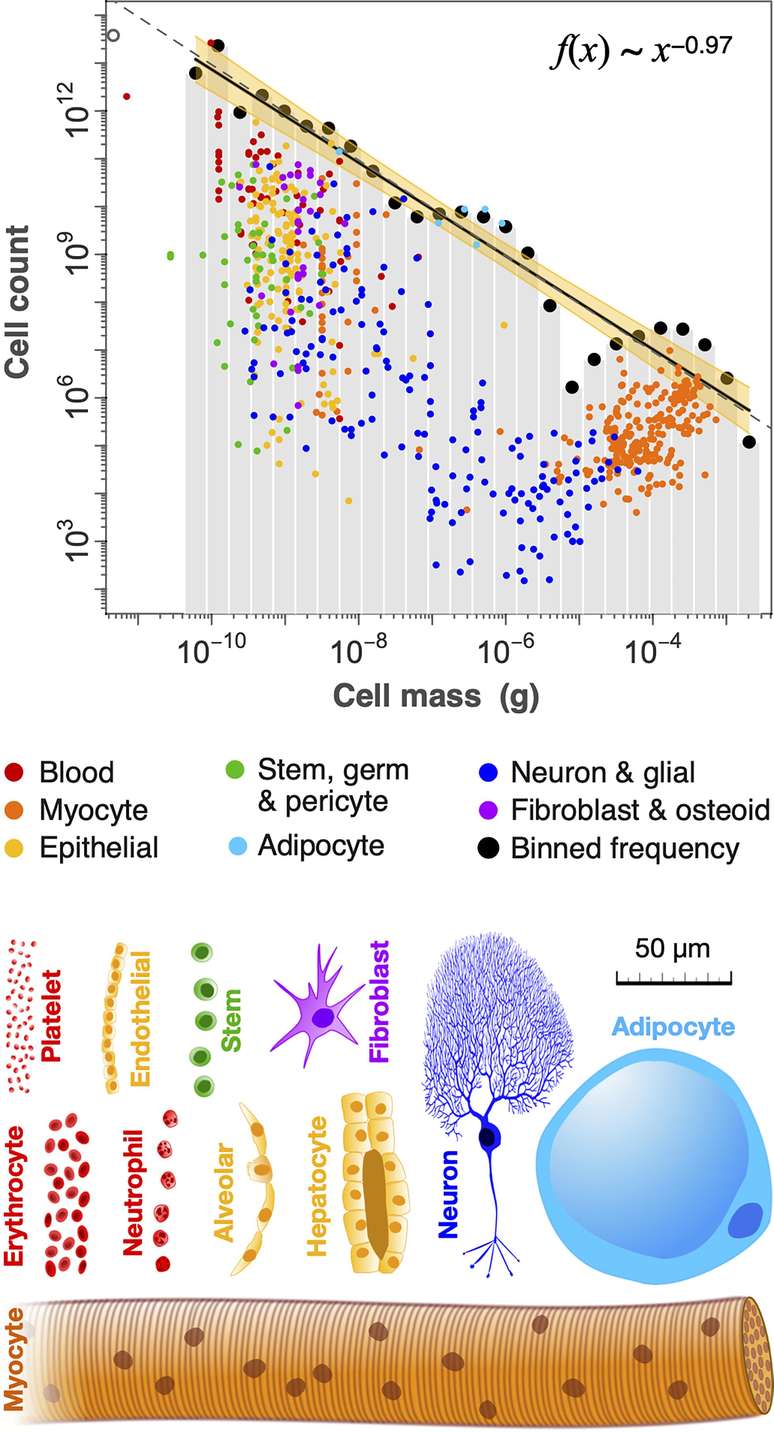
Therefore there is still a long way to go it can map and understand how the regulation, formation and distribution of cells in our body occurs.
For researchers, understanding how this balancing mechanism occurs is essential to the advancement of medicine and health technologies.
Want to know more about the human body and how it works? So, find out what the human microbiota or microbiome is.
Source: Terra
Rose James is a Gossipify movie and series reviewer known for her in-depth analysis and unique perspective on the latest releases. With a background in film studies, she provides engaging and informative reviews, and keeps readers up to date with industry trends and emerging talents.