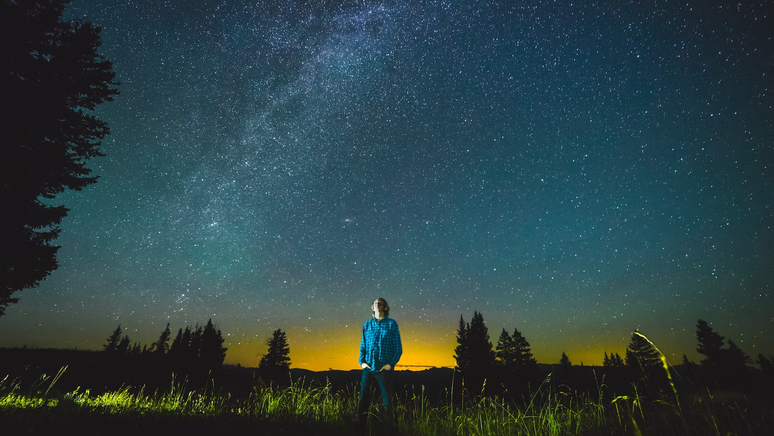
December comes with several astronomical events, such as the Geminid meteor shower, a conjunction between the Moon and Jupiter, and the start of summer. learn more
The last month of the year comes with very different astronomical events. In the next few days you will be able to see the brightness of Mercury, a Meteor shower and the arrival of summer, marked by the summer solstice.
- How to distinguish stars, planets and satellites in the night sky?
- 2023 Sky | This year, conjunctions of the planets and the solar eclipse are highlighted
OR Canaltech has collected the main astronomical events of the month of December, as well as indications for observing them in the sky. Let’s go?
Astronomical events in December
The year ends with Mercury at its maximum elongation, providing a good time to observe it during the early evening. The Geminid meteor shower and a conjunction between the Moon and Jupiter also occur.
Maximum elongation of Mercury (04/12)
Mercury reaches its maximum elongation at 11:00 am, making it the furthest from the Sun from our perspective on Earth. To observe the planet you have to wait until sunset; so, look for it in the west, shining brighter than most nearby stars.
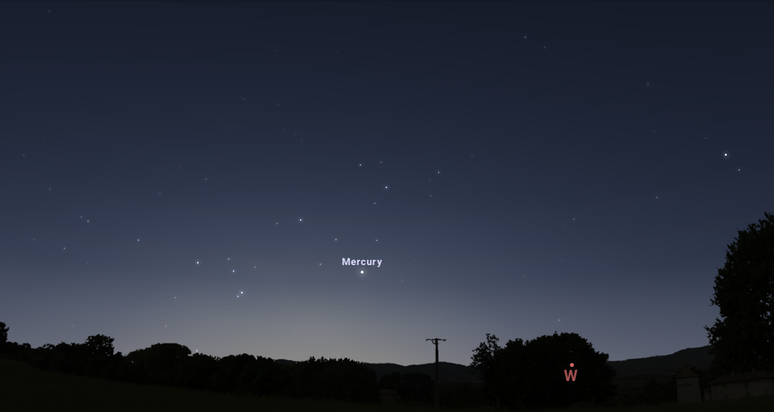

The planet remains visible until around 8pm. It’s worth taking the opportunity to see it, after all Mercury is closer to the Sun than our planet, and ends up being overshadowed by the star’s light. Therefore, its greater angular distance from the Sun facilitates observations.
Peak of the Geminid meteor shower (12/14)
A Geminids meteor shower It is considered one of the most spectacular events of the year and is caused by fragments of the asteroid 3200 Phaeton. It begins in November, but its meteors remain visible until December and its peak is expected to occur between the 13th and 14th, providing up to 120 “shooting stars” per hour.
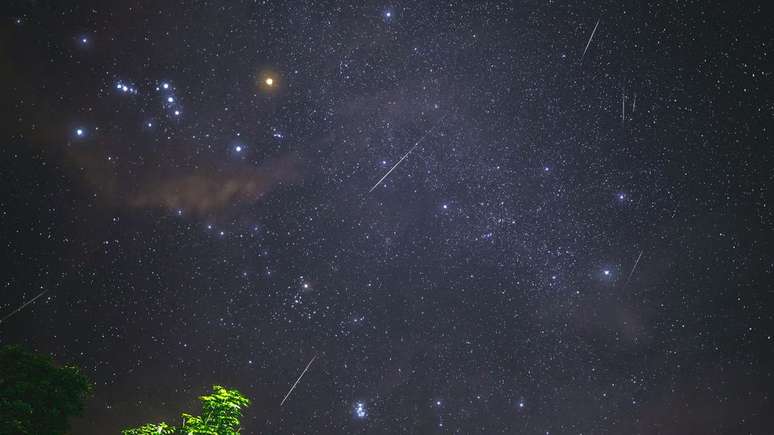

To observe it, look for the radiant (the direction from which the meteors appear to come) towards the constellation Gemini, the Twins. Although it is best observed in the Northern Hemisphere, it is also possible to observe Geminid meteors in the Southern Hemisphere.
Summer Solstice (22/12)
The summer solstice occurs in the Southern Hemisphere at 00:27. The event marks the beginning of summer here, accompanied by the longest day of the year. In the northern hemisphere the opposite happens: winter begins there and the longest night of all will occur in 2023.
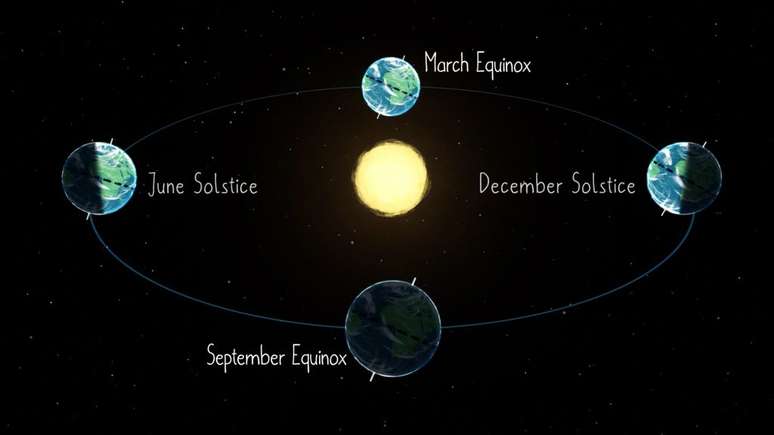
The solstice occurs because the Earth rotates around the Sun at an inclination of 23.5º, causing the hemispheres to receive different amounts of light throughout the year.
Conjunction between the Moon and Jupiter (12/22)
The year comes to an end with a conjunction between Jupiter and moon. During the event, the stars appear very close to each other from our perspective and can be observed with the naked eye.
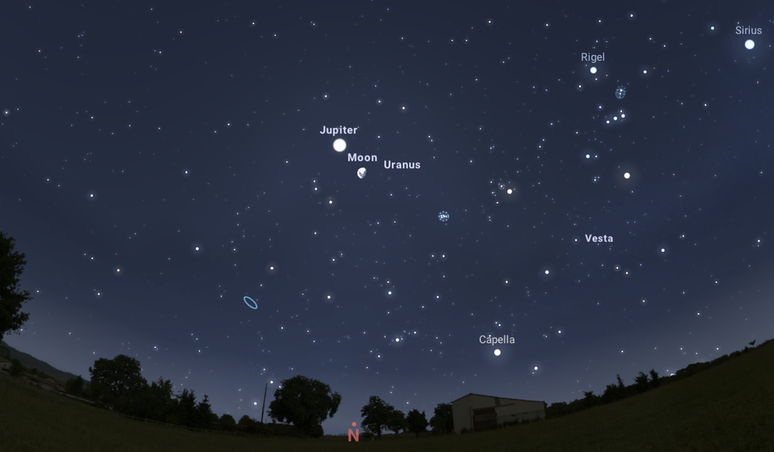
To see them, look east at the Moon and Jupiter after sunset: they remain visible until around 2 am, and then disappear below the horizon.
Moon phases in December 2023
Below you can see the main ones lunar phases during the month of December and the time at which each event takes place:
- December 5, at 2:49: First quarter moon
- December 12, at 8.32pm: New moon
- December 19, at 3.39pm: First quarter moon
- December 26, at 9.33pm: full moon
Trends on Canaltech:
- The drone captures the sensational maneuver of a giant ship in the port of Santos
- Pika 1.0 is the new version of AI that creates and edits videos
- 10 AI to create images from text for free
- The 50 funniest Google Assistant jokes
- Geographic discovery reveals how pyramids were built in Egypt
Source: Terra
Rose James is a Gossipify movie and series reviewer known for her in-depth analysis and unique perspective on the latest releases. With a background in film studies, she provides engaging and informative reviews, and keeps readers up to date with industry trends and emerging talents.







