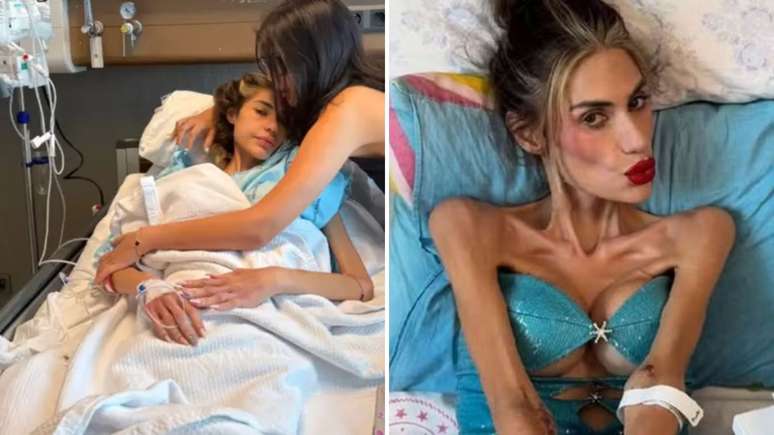
The influencer with 22.5 kg died after a long battle against anorexia; See the explanation of nutritionist Lucas Moraro
A 30 -year -old Turkish influencer died this month with a weight of only 22.5 kg. Nihal Candam fought anorexia nervosa and spent the last days of his life in the hospital with a very serious painting of malnutrition, but he could not resist. In conversation with the Novelthe nutritionist Lucas Moraro He explained how psychiatric disorder can worsen so much to the point of taking his own life.
Treatment of anorexia
Anorexia is one of the three most common eating disorders, killing about 160,000 victims per year (data of British and Danish studies). According to the nutritionist, the treatment is multidisciplinary, that is, it takes several professionals to treat a patient with a condition like the Nihal. In general, people with anorexia need psychologists, psychiatrists, nutritionists, physical educators and some doctors depending on the aggravation of the case.
Moving Explains that, first, you have to make an anamnesis in the person: “Where we face the history of food (models, preferences, aversions, compulsions, restrictions), weight history and BMI, physical symptoms (such as weakness, hair loss, gastrointestinal problems), food behaviors at risk (use of laxatives, prolonged fasting, car vomiting -nolesta) and nutritional status (laboratory test (anthropometric evaluation) ..
So you have to make a food and nutritional education: “By re -educating the patient on food myths, food functions and the importance of nutritional balance. We emphasize that all food groups play their role, fighting in these common paintings” food phobia “.
The third step, according to the professional, is to process a food plan supported by the three main pillars:
1- Flexible and adapted: Respect the treatment phase and the level of food resistance of the patient.
2- progressive: It begins with small and realistic objectives (such as structured meals, for example).
3- focused on calories or weight initially: The goal is to normalize food and reduce compensatory behavior.
Moving He underlines that the nutritionist should introduce few to small changes in the patient’s life: “Gradual food exposure (to reduce dietary fears), structured and regular meals (3 main snacks + 2-3), qualitative food diaries (to observe the emotions associated with consumption, without calorie concentration) and reintroduction of avoided foods.”
“After these passages we started teamwork, in a multidisciplinary way, acting in collaboration with psychologist, psychiatrist and clinical doctor. Nutritional strategies are aligned with psychotherapeutic treatment, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (TCC), which is fairly effective for TA”, explained.
The nutritionist also states that attention is not on the patient’s weight loss: “The goal is not weight loss (except in cases of obesity and clinical risk), but healthy relationship with food and body. The acceptance of the body and listening to signs of hunger and satiety are stimulated. The focus is always in behavior and not only in weight.”
Risks of anorexia
Like any disease, anorexia has very serious risks, especially physical. Moving Cites the 10 main risks of this disorder;
1- Neurological impromptu.
Mental confusion, difficulty concentration; Risk of hypoglycaemia coma; Cerebral atrophy observed in image exams.
2- cardiac failure.
Grave bradycardia (very slow heartbeat); hypotension (very low pressure); Cardiovascular collapse: the heart can no longer pump the blood correctly.
3- Hypothermia and intolerance to the cold.
The body loses the ability to maintain the temperature due to the lack of fat and metabolic deceleration.
4- Hydroelectrolytic imbalances.
Dangerous levels of sodium, potassium, phosphorus and magnesium; It can cause fatal cardiac arrhythmias; Feedback risk syndrome if nutrition is taken abruptly.
5- Hosteopenia/severe osteoporosis.
Accelerated bone loss, very high risk of fractures; Irreversible in many cases, even after weight gain.
6- Atrophy organs.
Liver, kidneys and heart decrease in size and function; It can evolve in more insufficiency of the organs.
7- impromptu immunological.
Recurring and serious infections; The body can no longer defend itself from bacteria or common viruses.
8- Amenorrhea and infertility.
Lack of menstruation for months or years; Reproductive hormonal axis impairment of the axis.
9- Gastrointestinal problems.
Gastroparesis (slowness of the slow stomach); chronic constipation; Feeling of early satiety.
10- And finally, the real risk of death runs.
Anorexia nervosa has the highest mortality rate among psychiatric disorders. The serious malnutrition (as at 22 kg) can lead to sudden death, in particular by cardiac arrhythmia or systemic infection.
Source: Terra
Ashley Fitzgerald is a journalist and author at Gossipify, known for her coverage of famous people and their lives. She writes about a wide range of topics, including celebrities, influencers, social media stars, and public figures. Her articles are known for their in-depth analysis and unique perspective. She is respected for her ability to keep readers up to date with the latest news and trends of the famous people.