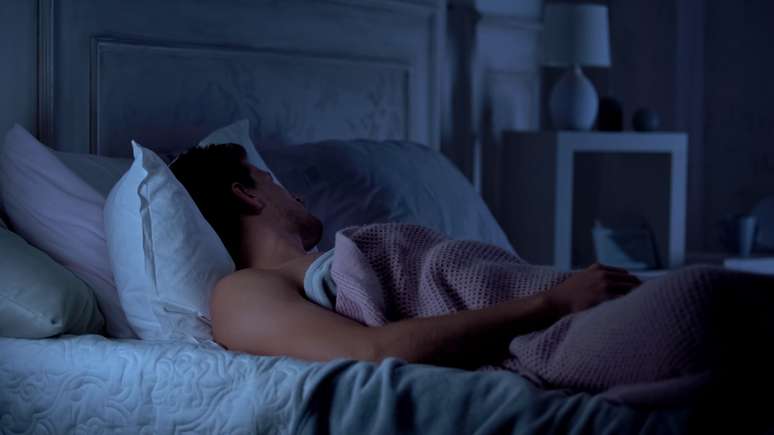
During this stage of sleep, our body removes unwanted materials from the brain.
Research published this week reveals that not sleeping deeply enough may increase the risk of dementia in the future. The conclusion is made by a team from Monash University, Australia, together with researchers from Harvard University, in the USA, and McGill, in Canada.
During deep sleep, also known as “slow-wave sleep,” the body removes unwanted materials from the brain, including the protein beta-amyloid, a signal that has been linked to Alzheimer’s disease.
The recent work, published in the journal Jama Neurology, had 346 people who were, on average, 69 years old. They had completed two sleep studies dating back to the 1990s. After 17 years, 52 participants developed dementia.
Each percentage decrease in slow-wave sleep each year was associated with a 27% increase in the risk of developing dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease (one of the most common types of dementia).
What is deep sleep?
Sleep can be divided into two groups: non-REM sleep and REM sleep. The first involves three subphases (N1, N2 and N3), the last of which is deep sleep, the one in which it is most difficult to awaken. In general, people go through several complete cycles, including all phases, while they sleep.
N1
This phase of non-REM sleep is the typical transition from wakefulness to sleep and usually lasts only a few minutes. It is the lightest phase of sleep and people who wake up often don’t realize they were actually sleeping. During this phase, eye movements are generally slow, heart rate and breathing slow, and muscles begin to relax.
N2
This later stage of non-REM sleep comprises the largest percentage of total sleep time and is still considered a light sleep stage from which we can easily awaken. In this phase we have a slower heartbeat and breathing, without eye movements, as well as a drop in body temperature.
N3
This is the deep sleep phase in which the body performs a number of important health-promoting tasks. In this phase the body is completely relaxed, the immune system is strengthened, tissue repair and cell regeneration occur, among other phenomena.
REM sleep
Only after these three phases is what is called REM sleep achieved, which occurs approximately an hour to an hour and a half after sleep. It is in this phase that there is a greater tendency to have vivid dreams. In general, the first time lasts about 10 minutes, increasing with each REM cycle: the last cycle of this phase can last approximately 30 to 60 minutes.
During this phase, breathing and heart rate increase and become more variable, and brain activity increases.
How to get deeper sleep?
According to the National Sleep Foundation in the United States, to get deeper sleep and better overall sleep quality, you should:
- Always sleep and wake up at the same time, even on weekends.
- You manage stress and anxiety better, especially when it’s close to bedtime. Relaxation techniques such as yoga and meditation can also be helpful.
- Do physical activity regularly, preferably during the day, in contact with natural light.
- Limit caffeine and alcohol consumption, especially from mid-afternoon onwards.
- Take care of your sleeping environment, which means keeping the room at a pleasant, quiet temperature and as dark as possible.
- Don’t bring electronic devices to bed as they can compromise the quality of your sleep.
Source: Terra
Ben Stock is a lifestyle journalist and author at Gossipify. He writes about topics such as health, wellness, travel, food and home decor. He provides practical advice and inspiration to improve well-being, keeps readers up to date with latest lifestyle news and trends, known for his engaging writing style, in-depth analysis and unique perspectives.