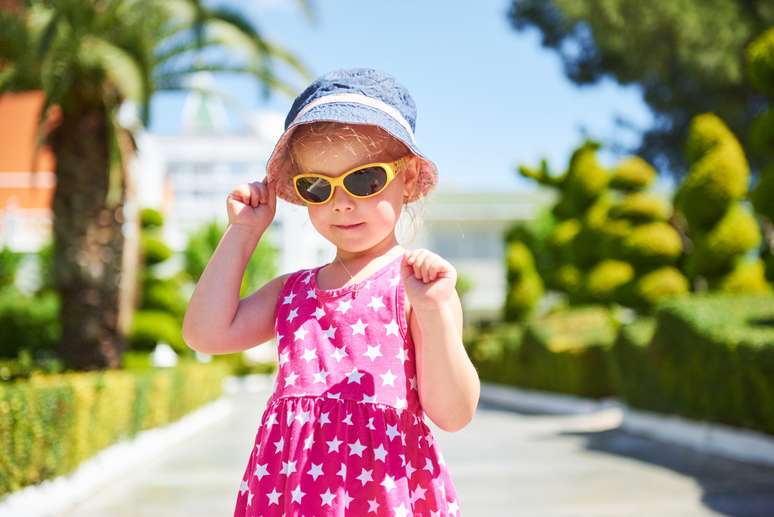
Up to six months of age, the use of sunscreen is not recommended; Clothing with UVA protection is the solution to avoid sunburn
Protection from sun damage is another one of those habits that should be taught from an early age. After all, the effects of sun exposure They are cumulative: sunlight and ultraviolet radiation received from childhood to adulthood will have lifelong consequences. The main risk factor for the development of skin cancer is precisely early exposure to UVA and UVB rays .
But how can we protect our little ones from this daily risk? It depends. Babies under six months of age cannot use sunscreen: at this age, in fact, sun exposure is not even recommended. Since the skin is more sensitive in the early stages of life, children are more susceptible to both sunburn and allergic reactions to sunscreen.
When can my child use sunscreen?
In 2017, news that an Australian baby had been hospitalized with an allergic reaction to sunscreen set off alarm bells among parents around the world. Doctors’ first warning was that at this age, the baby should not be exposed to direct sunlight.
Always stay in the shade and use covered strollers, as well as long clothes that protect legs and arms. Children’s skin is very delicate and can absorb chemicals in sunscreens. Since the immune system is also developing, any allergic process is more complicated at this stage.
After the first six months, children can use a special sunscreen for their age group: in pharmacies there are “baby” options. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, products with zinc oxide and titanium dioxide are good options, as they act as blockers that reflect radiation and are less likely to irritate your baby’s skin. Sunscreens should be broad-spectrum, meaning they block both ultraviolet A and ultraviolet B radiation.
Products intended for adults are at a higher risk of causing allergic reactions, even for children over six months of age. Looking for hypoallergenic options is also a good idea.
Before using any product, be it sunscreen or even moisturizer, test it on a small patch of your baby’s skin. If there is an allergy, it should show up within 48 hours – after which you should notify your pediatrician.
From six months to one year of age, children should only sunbathe for short periods and use sunscreen. Even with sunscreen, children should still wear clothing with good coverage and hats when going on longer walks or going to the beach and swimming pool. Another rule is to avoid the hours of maximum sun incidence, between 10:00 and 16:00. An important warning is that chlorine can also damage children’s skin, so even from six months onwards, be careful in swimming pools.
If your child gets sunburned, remove him or her from the sun immediately, apply cold compresses, and call your doctor. Do not wash the burn area with soap or apply any type of product before reaching the emergency room.
What is the ideal SPF for children?
Sun Protection Factor (SPF) is the number that indicates how long you can stay in the sun before suffering damage from exposure. What differs between products, therefore, is the reapplication time for each of them.
The minimum recommended SPF is 30, which should be reapplied every two hours. Sunscreens should also be reapplied whenever the child comes into contact with water or sweats a lot.
The recommended amount of filter is, for children, four teaspoons for the head, four for the front of the torso, four for the back. Two teaspoons should be applied to each arm and 3 teaspoons to each leg.
What about vitamin D?
To ensure that children have enough vitamin D, it is recommended to take vitamin supplements duly recommended by the pediatrician, where applicable. The vitamin ensures healthy bones and other important functions in the body. However, to synthesize the vitamin, it would be necessary to be exposed to ultraviolet B radiation during peak hours. The Brazilian Society of Pediatrics advises against this exposure, even if it is intended to ensure vitamins.
Source: Terra
Ben Stock is a lifestyle journalist and author at Gossipify. He writes about topics such as health, wellness, travel, food and home decor. He provides practical advice and inspiration to improve well-being, keeps readers up to date with latest lifestyle news and trends, known for his engaging writing style, in-depth analysis and unique perspectives.