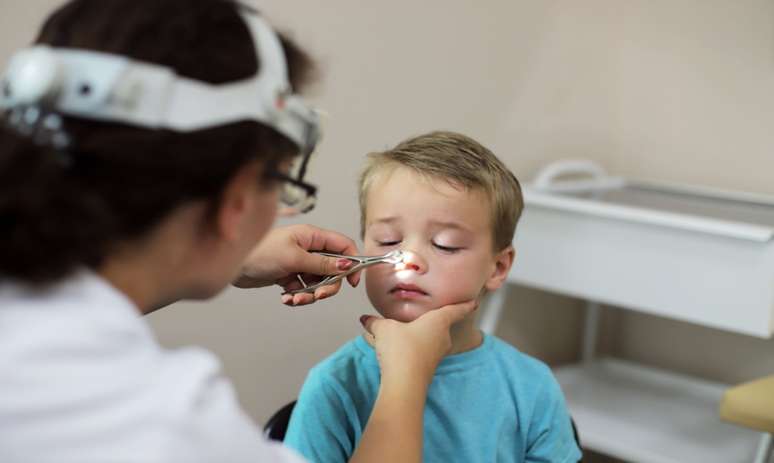
Adenoid hypertrophy, better known as spongy meat, causes many inconveniences on a daily basis. In addition, without proper treatment, it can cause health complications. In this sense, adenoid surgery appears as a solution. Spongy meat The adenoid is a small structure located behind the nose, just above the palate. […]
Adenoid hypertrophy, better known as spongy meat, causes many discomforts on a daily basis. In addition, without proper treatment, it can cause health complications. In this sense, adenoid surgery appears as a solution.
spongy meat
The adenoid is a small structure located behind the nose, just above the palate. When it hypertrophies, it becomes an obstruction that compromises breathing. Therefore, it is common for patients to have a stuffy nose and a nasal voice.
Furthermore, the condition is associated with growth problems in childhood, as well as snoring, apnea, daytime tiredness, agitation, irritability, hyperactivity, difficulty concentrating – and also includes problems with misalignment of the dental arches, bruxism and, even, coughing, ear infections and sinusitis.
Therefore, for many children, removing this small structure is the most assertive recommendation to remedy the dysfunction.
Adenoid surgery
“The choice of whether or not to perform surgery depends mainly on the size of the adenoid. In other words, how much this spongy flesh interferes with the structures of the face,” explains Gilberto Ulson Pizarro, an otolaryngologist at Hospital Paulista.
“If it is medium or small in size, clinical treatment with drugs is indicated, without the need for surgery. In the most serious cases, removal is undoubtedly the best thing to do,” adds the doctor.
Much less invasive
For patients who are advised to undergo surgery, the doctor believes that today the procedure is much less invasive than in the past. Therefore, rehabilitation is also faster.
“Advancements in imaging techniques and the adoption of new tools, such as the microdebrider, allow surgical interventions to be performed with just the touch of the fingers, ensuring greater safety in controlling bleeding, as well as making it more precise, without leaving residues that could cause the process to repeat itself,” he underlines.
As for recovery, the specialist explains that there have been advances compared to the past. “Adenoid surgery, without tonsil surgery, is now much safer and has a quicker recovery, reducing the time it takes for the child to eat again and return to normal activities. Generally, most children recover from adenoid removal in one to two weeks.”
When to undergo surgery
As for the decision on surgery, the doctor specifies that it depends more on the damage caused by the adenoid than on the patient’s age.
“There are cases of newborns, for example, in which the adenoid ends up obstructing the ear canal. In these types of situations, the intervention must be performed regardless of age. However, in cases in which the adenoid only interferes with breathing, it is possible to wait until the child is 3 years old, if he does not present symptoms associated with obstructive sleep apnea,” he explains.
The risks are minimal, as long as the necessary precautions are taken. “Every surgical procedure requires care. That is, preoperative tests performed and evaluation by a doctor, be it a pediatrician or a cardiologist. In the case of adenoids, the procedure is very safe. It has a lower risk of bleeding of more than 2% and the risks associated with anesthetics and other problems are less than 1% in children without comorbidities,” concludes the professional.
Source: Terra
Ben Stock is a lifestyle journalist and author at Gossipify. He writes about topics such as health, wellness, travel, food and home decor. He provides practical advice and inspiration to improve well-being, keeps readers up to date with latest lifestyle news and trends, known for his engaging writing style, in-depth analysis and unique perspectives.