Studies show that honey helps beneficial bacteria survive in the gut
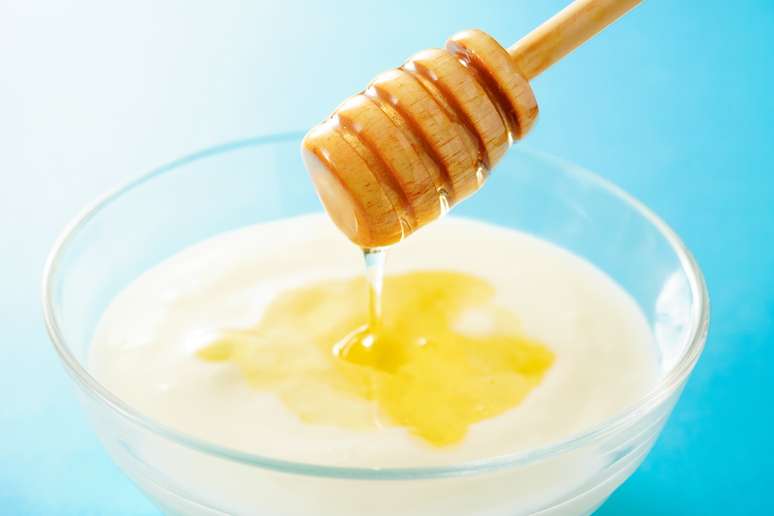
Yogurt is known for containing probiotics, but how many of them actually reach your gut? New research shows that a common and delicious combination may help good bacteria pass through your intestinal tract intact.
Two separate studies have found that adding honey can help yogurt probiotics survive during digestion. Since enzymes in the gastrointestinal tract can sometimes kill beneficial microorganisms, this may be a useful strategy to keep them alive.
Both works were conducted by researchers at the University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign and published in March and August in The Nutrition Journal.
Survival of bacteria
According to study author and associate professor of nutrition Hannah Holscher, interest in the effects of honey in yogurt began after finding research showing that honey helped bifidobacteria survive in laboratory experiments.
“Since bifidobacteria are common probiotic bacteria added to yogurt and plain yogurt is commonly consumed with honey, I was interested in determining whether this culinary combination could help support probiotic survival both in vitro and in vitro. [no laboratório] as in real life [em pessoas]”, he told the site Health. Holscher’s suspicions were confirmed by the results of both studies.
Effects of different types of honey
The first of Holscher and colleagues’ studies was a laboratory experiment that examined how four different types of honey affected the viability of probiotics in yogurt: clover, alfalfa, buckwheat, and orange blossom honey were added to yogurt containing the probiotic strain. Bifidobacterium animalis.
The researchers then tested the effects of supposed human digestion, adding simulations of saliva, stomach acid, intestinal bile, and enzymes. In the intestinal phase of this simulated digestion, the clover honey yogurt had the highest probiotic survival rate.
Why clover honey?
According to the researcher, there are probably several reasons for the unique effectiveness of clover honey. One hypothesis is the higher amount of glucose in clover honey. “The glucose could have served as an energy source for the probiotic bacteria,” he noted.
Additionally, clover honey has lower amounts of enzymes that break down sugars into oligosaccharides, which bacteria can use for energy. Therefore, the lower enzyme concentrations in clover honey could have meant more energy to feed the probiotic bacteria during the long journey through the intestinal tract.
Clover honey also contains antioxidants that may have protected the probiotics from the harsh environment of the small intestine.
Human trials
To find out if these findings applied to humans, Holscher’s team conducted a second study. Over a two-week period, 66 healthy adults were assigned to consume either yogurt with honey or yogurt with added sugar. Participants provided stool samples, information about their bowel habits, and completed questionnaires about mood and cognition.
After two weeks, it was clear from the stool samples that the honey yogurt had enriched the stool. B. animalis throughout digestion. According to Holscher, a spoonful of honey would be enough to support the survival of probiotics.
Impact on intestinal transit
However, she noted that while honey appeared to keep the probiotics alive, it did not affect intestinal transit time, nor did it have any other observable health benefits, such as improved bowel habits, mood, or cognition.
According to Holscher, the lack of significant improvements in gut health in participants in the second study doesn’t mean honey isn’t a worthy addition to yogurt.
“This may be because the study participants had relatively normal digestive health, so there wasn’t much room for improvement,” she said.
If they suffered from constipation, they may have found a benefit in speeding up their intestinal transit time by consuming honey yogurt.”
Future studies may clarify whether people with constipation might notice an improvement in digestion time by adding honey to yogurt.
Advantages and disadvantages of using honey
In moderation, honey can also be considered a nutritious food in its own right. The food also contains potassium and phenols, which are also being studied for their possible influence on the gut microbiome.
The problem is that honey is a type of added sugar, which can lead to weight gain and its consequences. Since it is of animal origin, it is not included in the vegan diet. Honey is also contraindicated for those suffering from diabetes, fructose intolerance and for children under 1 year old.
So don’t overdo it. On a 2,000 calorie a day diet, the recommendation is to consume less than 200 calories from added sugars. A tablespoon of honey provides about 64 calories. So if you decide to add honey to your yogurt, limit other sources of added sugar on the same day.
Source: Terra
Ben Stock is a lifestyle journalist and author at Gossipify. He writes about topics such as health, wellness, travel, food and home decor. He provides practical advice and inspiration to improve well-being, keeps readers up to date with latest lifestyle news and trends, known for his engaging writing style, in-depth analysis and unique perspectives.