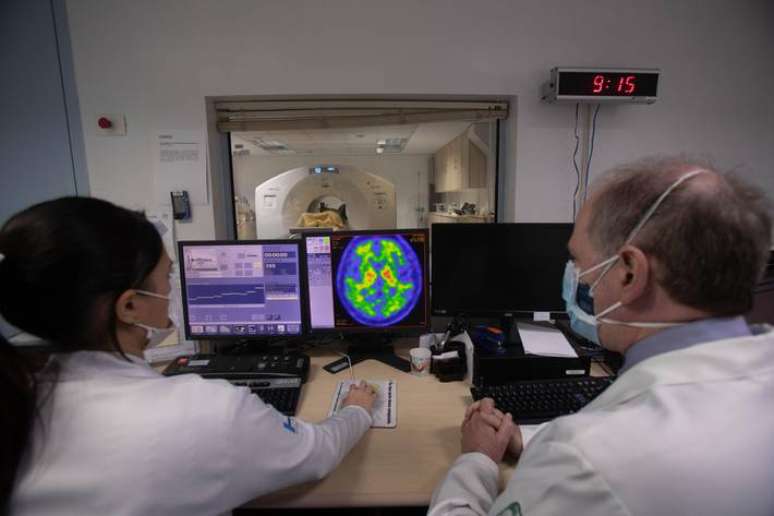
The study took into account almost 25,000 cases and stated that the conditions of the disease are progressive
A group of researchers from the University of Los Angeles (UCLA) has identified that there are four distinct paths that lead patients to Alzheimer’s disease.
Receive the main news directly on WhatsApp! Sign up for the Earth channel
The study took into account almost 25,000 cases collected at the Health Bank of the University of California.
“Unlike previous research focused on individual risk factors, the UCLA analysis has mapped the sequential diagnostic models that revealed how the conditions progress step by step towards Alzheimer’s disease,” said the university in a note.
With the research it was possible to determine four primary common factors in cases:
- Mental health path: psychiatric conditions that lead to cognitive decline
- Encephalopathy path: Conditions of cerebral dysfunction that increase over time
- Light cognitive route for compromise: gradual progression of cognitive decline
- Vascular disease: cardiovascular conditions that contribute to the risk of dementia
“In any case, it has presented several characteristics and demographic clinics, suggesting that different populations can be vulnerable to different progression routes,” said the university.
The study discovered that about 26% of diagnostic progressions had a coherent directional system. The example used was the hypertension that often preceded depressive episodes, which increased the risk of Alzheimer’s.
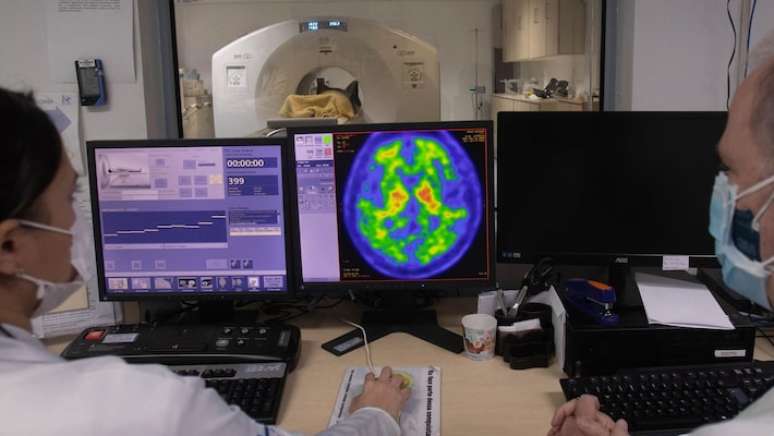
“Recognizing these sequential models rather than focusing on diagnoses in isolation can help doctors improve the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease,” said the main author Dr. Timothy Chang, assistant professor of neurology at the Ucla Health.
The researchers expect Discovery to help professionals to identify patients with high risk first in the progression of the disease, they interrupt harmful sequences before advanced and adapt strategies based on individual road models.
Source: Terra
Ben Stock is a lifestyle journalist and author at Gossipify. He writes about topics such as health, wellness, travel, food and home decor. He provides practical advice and inspiration to improve well-being, keeps readers up to date with latest lifestyle news and trends, known for his engaging writing style, in-depth analysis and unique perspectives.