Understand what is the predisposition to develop thrombi, its risks and treatment modalities
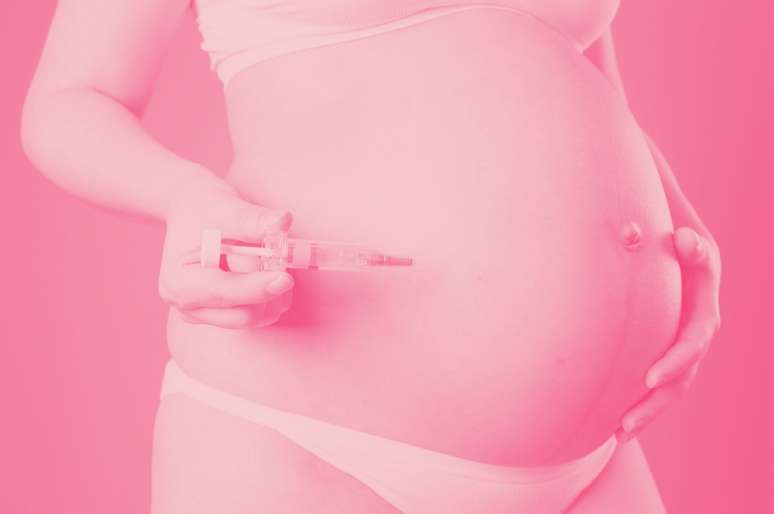
Thrombophilia is a genetic or acquired tendency of the blood to form thrombi, i.e. clots that block circulation in blood vessels.and it can be one of the challenges encountered during pregnancy.
“Women have this predisposition and pregnancy itself is a risk factor for thrombus formation“, explains David Pares, professor and head of the Department of Obstetrics at the Paulista School of Medicine of Unifesp (Federal University of São Paulo). The possibility of a blockade requires medical attention and care during the entire pregnancy.
symptoms of thrombophilia
“Thrombophilia itself, more often than not, is asymptomatic”, underlines Jéssica Trafani, gynecologist and obstetrician of the Mantelli Clinic. The risk of the painting varies widely. You can go to one thrombosis in the legs and other regions of the body – whose main symptoms are swelling, pain, redness and heaviness – to more serious situations, such as thromboembolismwhen the thrombus detaches from the place where it was formed and goes to the lung, a serious condition that can lead to death.
“When thrombophilia causes some repercussions during pregnancy, it is usually accompanied by infertility, repeated miscarriages, thrombosis, placental microthrombi formation, and complications such as increased blood pressure during pregnancy,” says Jessica.
Can thrombophilia lead to pregnancy loss?
YES. As reiterated by Naira Scartezzini Senna, gynecologist and obstetrician at the Hospital e Maternidade São Luiz São Caetano, gestational loss related to thrombophilia usually occurs in early pregnancy. During this time, clots can impair the blood supply to the placenta and even before they appear. “The thrombus can form and prevent the implantation of the embryo in the uterus”emphasizes the doctor.
But later, some studies indicate that microthrombi could progressively block the flow of blood and nutrients to the fetus. “The answer to this is a decrease in the child’s growth rate and other serious intercurrences, such as fetal death,” Pares explains. There is also the possibility that the thrombus will once and for all block the passage to the placenta and placental abruption will occur, which also threatens the life of the mother and the baby.
But there is no official consensus on this matter. “There is insufficient evidence to say that thrombophilia causes fetal growth restriction and other adverse obstetric events”retorts Ana Kondo, midwife of the Hospital das Clínicas of the Faculty of Medicine of the USP (University of São Paulo).
In fact, a review on the subject, carried out by the University of Melbourne, Australia, evaluated 12 studies and concluded that most cases of thrombophilia are not related to events of this type. for that too not everyone needs to have this condition investigated.
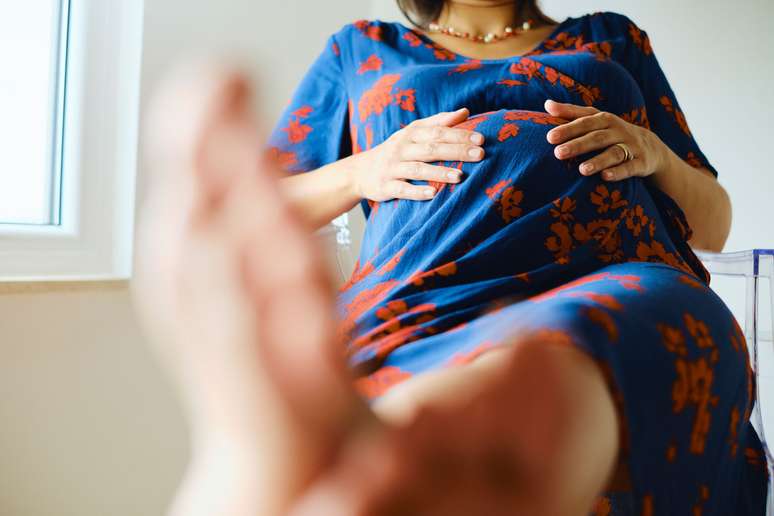

The thrombophilia investigation
According to the guidelines, only women with a family history of thrombophilia discovered during pregnancy or thromboembolic diseases, such as thromboembolism and deep vein thrombosis, should undergo the study. From three gestational losses, an examination can also be requested.
Other conditions increase your risk. “Women with obesity or severe movement limitations, such as wheelchair users, are also at a higher risk of developing thrombosis during pregnancy,” Naíra points out. But, for these, there is no formal recommendation of the test, as well as in cases of growth restriction and placental abruption in previous pregnancies.
“The cost of treatment is high and the diagnosis can cause unnecessary heartache, such as not always having the bias will lead to some problems“, explains Ana Kondo. The position is strengthened by medical societies, which contraindicate mass screening.
The test to find out if a woman has thrombophilia is done through a blood test., which looks for genetic mutations related to blood clotting – there are two causing the problem. “Other autoimmune alterations cause the body to produce enzymes that act in coagulation and also appear in the result,” Pares points out.
After the diagnosis, the woman can be referred to evaluation by a vascular surgeon and a hematologist, but you won’t necessarily have to follow these specialties. It all depends on the obstetrician’s familiarity with the subject.
continuous treatment
There is no magic formula except daily injections of enoxaparin, an active ingredient that blocks clotting. They are given at home, by the woman or her family, in the belly or inside the leg, and the doctor may increase the dose if necessary, such as before air travel or other situations in which the risk of clots is greater.
Treatment is offered by the public network, but it can take some time, which means that carriers of the condition have to pay a high cost, over R$ 200 for a box with two syringes. Unfortunately, measures such as rest, food or other lifestyle measures have little effect on the development of the disease.
“There’s not much you can do when the alteration is genetic, but it can avoid associated factors, such as obesity, maintaining ideal weight and physical activity, which by the way are not contraindicated, on the contrary”, he explains Pares.
On long journeys, by plane or bus, or periods of greater immobility, it is recommended put on special elastic stockings and get up every hour to move – or at least stretch and bend the foot. “But this should also be done by other pregnant women, as pregnancy itself carries this risk,” Pares explains.
Thrombophilia at the time of delivery
The fact that pregnancy increases the risk of blood clots is precisely a protective tactic of the body against natural childbirth. “After delivery, clotting factors increase to prevent bleeding and major bleeding,” Ana Kondo points out. Thus, in thrombophilia, as in most situations, normal delivery is the best choice, except when there are contraindications or delivery must be anticipated.
“In some cases the birth must be planned and discussed, but this depends a lot on what the genetic alteration is and on the severity, as well as on other health problems”, advises Pares. Whichever path you choose, you need to do a adjust the dressing a few hours before, as they act just like blood thinners and therefore increase the risk of bleeding.
The drug is kept until days after delivery, between 7 and 40, as the risk of blood clots remains higher.
Source: Terra
Rose James is a Gossipify movie and series reviewer known for her in-depth analysis and unique perspective on the latest releases. With a background in film studies, she provides engaging and informative reviews, and keeps readers up to date with industry trends and emerging talents.







