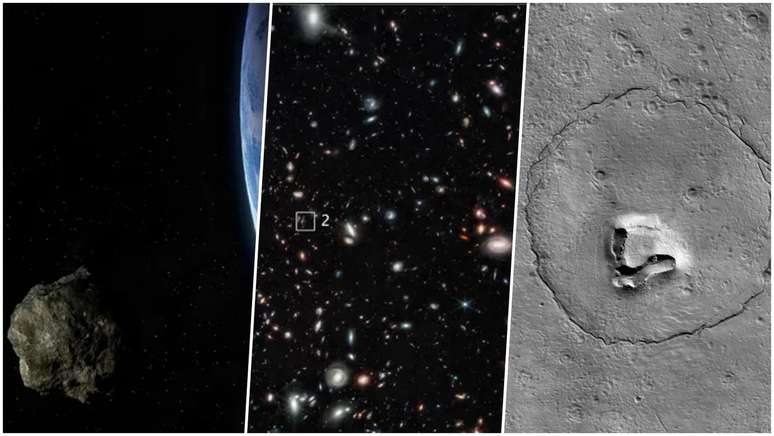
In the last week some space news has made headlines, such as the passage of the asteroid 2023 BU and the age of an ancient galaxy. Learn more!
This week, the passage of asteroid 2023 BU gave us something to talk about: during the “visit”, the space rock was only 3,600 km from the surface of our planet, posing no risk to us. Other topics that stood out include changes (or not) in the motion of the Earth’s core, new discoveries from observations by the James Webb Telescope, a beautiful crater on Mars, and much more.
Check it out below:
Earth’s central movement challenges scientists
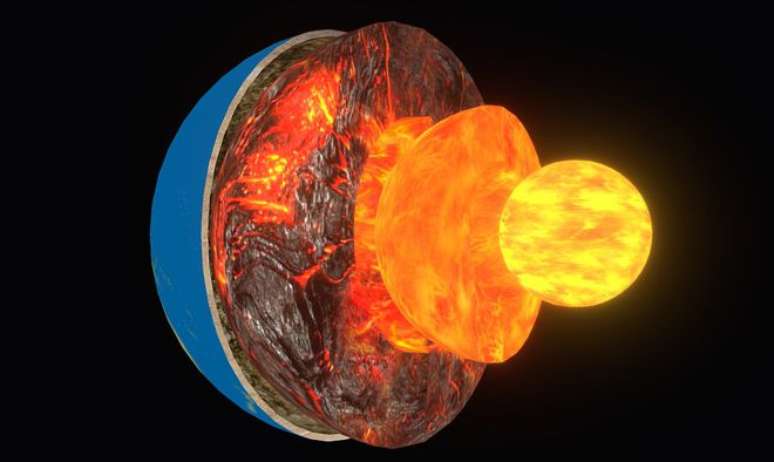

A study conducted by researchers at Peking University in China has brought results that have captured the attention of the scientific community and the public. The study suggests that Earth’s inner core, a Pluto-sized structure, would have stopped rotating along with the direction of rotation of the rest of the planet.
The issue is complex even among scientists, who have not reached a consensus on what is happening deep inside the Earth. Some even refute the claim, since scientific language is often misunderstood among laymen. Even so, it is certain that changes in the rotation of the core will not cause noticeable changes for us, who live in the earth’s crust.
- Understand all about the topic: Scientists refute the claim that the Earth’s core is standing still. Understand!
The asteroid was 3,600 km from Earth
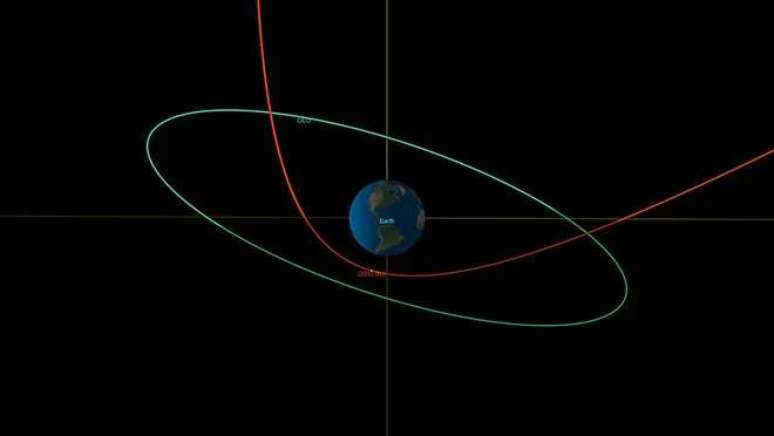
On Thursday (26), asteroid 2023 BU made its closest approach to Earth. During the flyby, the object was only 3,600 km from the surface of our planet: for comparison, consider that it has come closer than some of the geostationary satellites in Earth orbit!
One can breathe a sigh of relief, since the “visit” from space rock was not a cause for concern. After several analyzes of its orbit and size, scientists have concluded that it poses no risk to Earth – and even if it were on the path to a collision, it’s so small that it would probably burn up as it passed through the atmosphere. .
- Read the full story at: Asteroid 2023 BU is approaching Earth and is closer than some satellites
Operations with the James Webb tool are suspended

On January 15, the NIRISS (Near Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph) instrument on the James Webb Telescope experienced a communication delay. It has four modes of operation and can be used in a variety of ways, acting as a camera when other instruments are busy, searching for distant galaxies, and more.
NIRISS was developed thanks to a partnership between NASA and Canada’s space agency CSA, and members of both are investigating the incident. As a result, scientific operations of the instrument are temporarily suspended.
- Read the full story at: James Webb crashes and loses communication with the tool
Where do the waves created by the solar winds go?
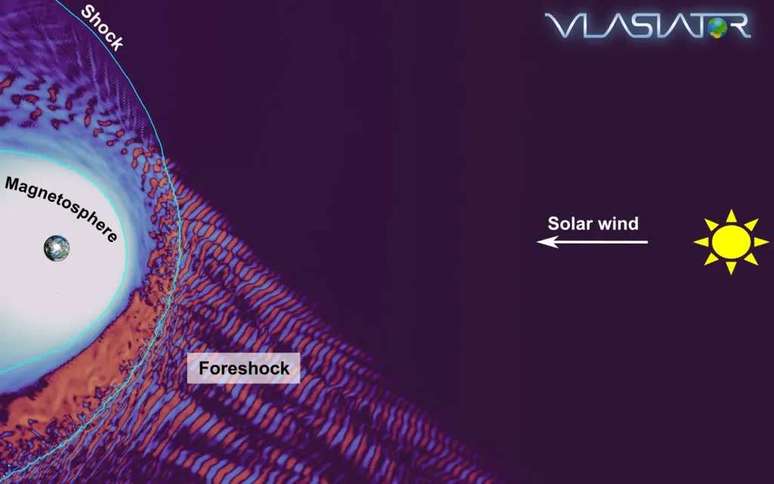
The Earth has a magnetic field, a complex and dynamic “bubble” that protects us from cosmic radiation and electrically charged particles. Some of these particles come from the Sun and cause small oscillations when they encounter the field. However, the scientists noticed something intriguing: these ripples appeared to be coming out of the magnetosphere, the area under the influence of the magnetic field.
To investigate this decades-old mystery, scientists investigated a hypothesis developed in the 1970s, which suggested a connection between the shock region, formed by interactions between the magnetosphere and the solar wind, and the region known as the “ante- shock”, where solar storms also occur.
- Read the full story at: 50-year-old mystery about Earth’s magnetosphere solved
“Catalogue” of compounds in the star-forming region

A team of astronomers used the James Webb Telescope to examine the Chameleon I molecular cloud, located about 631 light-years away. There is a star-forming region in full steam ahead there, and in addition to star formation, it also contains several molecules essential for life as we know it.
The telescope data revealed water, carbon dioxide, methane, ammonia and even methanol, the simplest of the complex organic molecules. The identification of the molecule suggests that the stars and planets that are born there will have molecules in a relatively advanced chemical state.
- Read the full story at: James Webb Telescope identifies organic molecule in molecular cloud
The light from this galaxy is almost 97% of the age of the universe
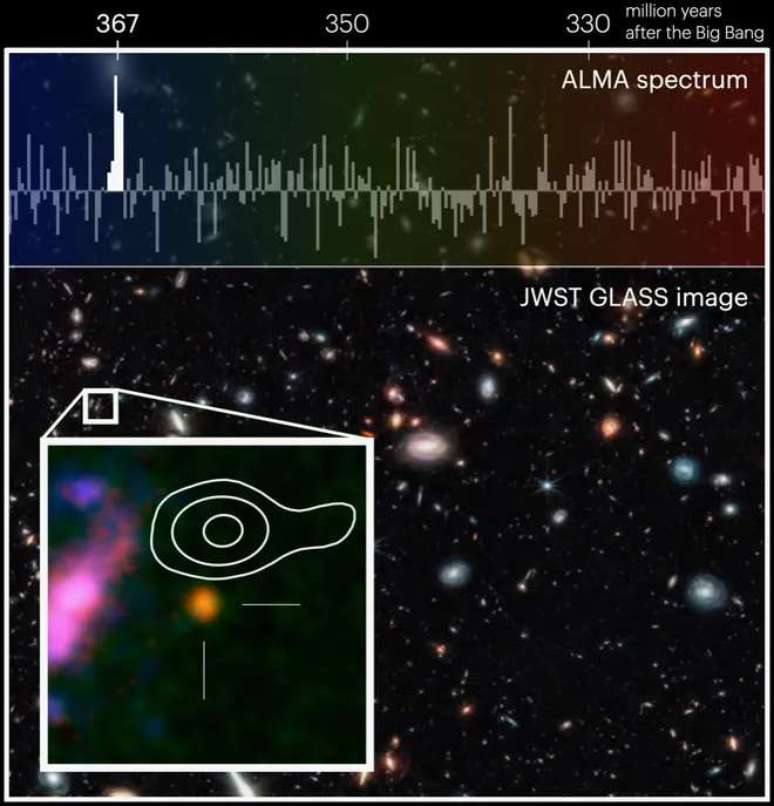
Last year, the James Webb Telescope led to the discovery of a possible group of early galaxies: one of these was the galaxy GLASS-z12, which appeared to exist 350 million years after the Big Bang. At the time, the researchers who announced the discovery stressed that new observations were needed to confirm the age of the galaxies.
Well, the new observations happened. With the ALMA radio telescope in Chile, the researchers confirmed that the light emitted by GLASS-z12 is almost 97% of the age of the universe, which confirms the existence of primordial galaxies discovered by Webb.
- Read the full story at: The distant galaxy seen by James Webb is confirmed to be old – and very old!
Another “different” crater on Mars
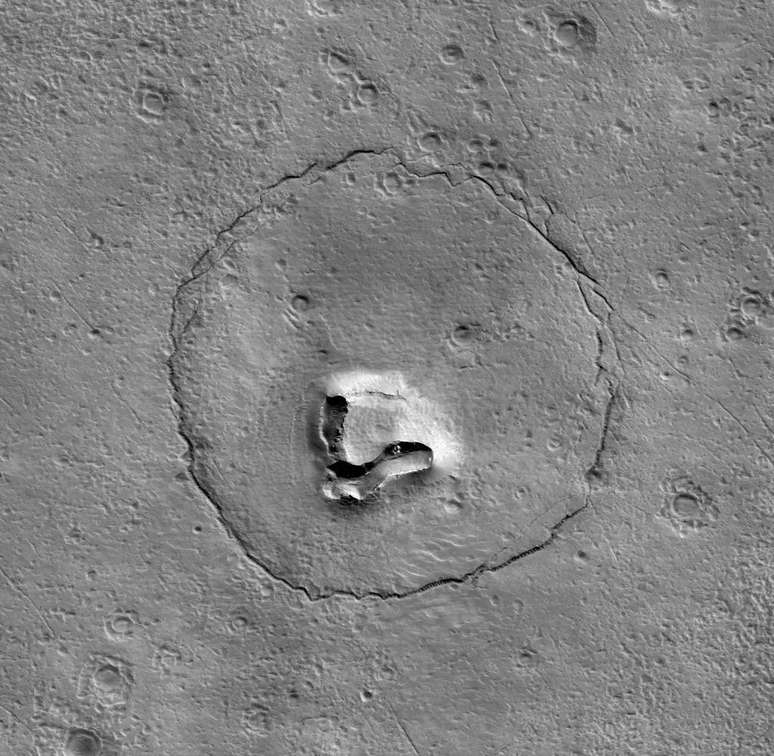

NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter has found a funny crater on Mars: As it orbited the nearby planet, it spotted a crater shaped like a bear’s head. The “Martian bear” derives from pareidolia, the phenomenon through which the human brain associates abstract shapes with those familiar to us.
It is not yet known for certain how the crater formed, but it is possible that the circular pattern derives from material deposited on top of an impact crater. The “nose” could be a volcanic opening.
- Read the full story at: Bear on Mars | NASA probe photographs a curiously shaped crater
Changes to Starlink satellites

It is no news that Starlink satellites, from SpaceX, raise concerns for the astronomical community: Since 2019, when the first ones were launched, scientists have drawn attention to the interference they cause in astronomical observations. Now, the company has struck a deal with the US National Science Foundation (NSF) to fix the problem.
SpaceX has agreed to take several measures to reduce the effects of satellites, such as solar panels to reduce glare, coatings that reduce light reflected from them, and more. In addition, the company has also committed to collaborating with interested radio astronomy facilities.
- Read the full story at: SpaceX will change the design of the Starlink so that it no longer harms astronomy
Other useful topics:
- How many stars are there in the Milky Way?
- Why are the planets round?
- Why do some people believe the moon is hollow?
Trending on Canaltech:
- Always thought strawberry dots were seeds? Found it wrong!
- The oldest art in the world was not created by humans
- Rocks formed from plastic are discovered on an island in Espírito Santo
- WhatsApp releases a new camera interface for everyone
- The photos show asteroid 2023 BU as it “scraped” past the Earth
- Probably the oldest mummy in Egypt, 4,300 years old, found in Saqqara
Source: Terra
Rose James is a Gossipify movie and series reviewer known for her in-depth analysis and unique perspective on the latest releases. With a background in film studies, she provides engaging and informative reviews, and keeps readers up to date with industry trends and emerging talents.








