The issue had repercussions on social media after an article by an English expert, but doctors warn that the association is not a rule and there is prevention
A association between oral sex AND cancer Sore throat has gone viral on social media in recent days, raising doubts among Internet users about the possibility of developing the disease through sexual intercourse. According to the experts consulted by the Stadium, the risk exists, due to Human Papillomavirus infectionthe popular HPV, which has carcinogenic potential. Despite this, they say, causality is not the rule and there are ways to prevent it.
The repercussion on the networks is due to a Article published by Professor Hisham Mehannaby the Institute of Cancer and Genomic Sciences of the University of Birmingham, England, on the portal The Conversation, last Tuesday, 25. In the publication, entitled “Oral sex is now the leading risk factor for throat cancer” in free translation, the expert points to a “rapid increase” in throat cancer in the West. According to him, this crescent is associated with HPV infection, fueling what some scholars have termed an “epidemic.”
With surprise and awe, Internet users reacted to the text, which was replicated on large Twitter profiles. Actress and presenter Nanny Werneck he entered the discussion in a good mood. “Please don’t say that,” she wrote. According to experts, the increase in the incidence of oropharyngeal cancer caused by HPV infection has indeed been observed in different parts of the world, especially in the last two decades.
please don’t tell https://t.co/pfEyxoi2xt
— Tata Werneck (@Tatawerneck) April 27, 2023
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) WE suggest that approximately 70% of oropharyngeal cancers in the country are HPV related. Also, before, the virus was mainly associated with cervical cancer, but among North Americans, the number of cases of HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer already exceeds the rates of cervical cancer from the same cause, according to Gilberto de Castro Junior, an oncologist specializing in lead and neck Syrian-Lebanese hospital.
One of the reasons given by science for this growth is precisely the decline in cases of oropharyngeal cancer caused by smoking and alcoholism, which are the other two main factors of the disease. “Historically, throat cancer has been associated with high cigarette and alcohol consumption. But at least in the last 20 years, especially in richer countries, there has been a progressive decline in smoking rates and, just as often as this decreases, it has been noted. It is known that throat cancers have not decreased in number, and many of them have been caused by HPV,” explains Virgilio Gonzales Zanella, head and neck surgeon at Santa Casa de Porto Alegre. According to him, the rates can also vary according to the sexual practices of each culture.
In the case of Brazil in general, smoking and alcohol abuse continue to be the main causes of the disease, according to Castro Junior. The numbers, however, may vary depending on the audience. “In the Unified Health System (Sus) the main risk factors are still cigarettes and alcohol. But among the more affluent socio-economic patients, in private healthcare, it is already observed that the virus is found in most cases”.
The relationship between oral sex and cancer is not a rule
Head and neck specialists point out that the relationship between oral sex and the occurrence of oropharyngeal cancer is not necessarily a universal sequence, for different reasons. In addition to the presence of viral infection in one of the partners, the relationship is conditioned by the HPV subtype.
“Not all papillomaviruses are the same. There are those with high oncogenic potential and those with low risk. Furthermore, if the virus arrives (in the throat), not everyone develops cancer. Just like any virus, you have an immune response to fight it,” explains the doctor from Sírio-Libanês. Among the more than 200 types of HPV, numbers 16, 18, 31 and 33 are recognized as oncogenic, that is, they can infect a cell and transform it in carcinogen, according to the professional.“The presence of the virus and the development of cancer are the exception, not the rule,” he adds.
Since the main route of transmission of HPV is intimate relationships, another decisive factor in the relationship is sexual behavior. Doctors emphasize that the use of condoms is essential to prevent infection, as well as other sexually transmitted diseases. “Since oral sex is common and the virus is widespread in the population, it is a question of risk. The more unprotected sex there is, the greater the exposure to infection,” emphasizes the oncologist.
In this sense, the number of sexual partners of a person can also be considered a risk factor, due to the increased exposure to the virus. The article that sparked the backlash of the discussion even cites research published in 2007 in the scientific journal The New England journal of medicine, which states that the main risk factor for the disease is the number of sexual partners over a lifetime, especially oral sex. The study states that people with six or more partners are 8.5 times more likely to develop oropharyngeal cancer than those who don’t engage in oral sex.
html[data-range=”xlarge”] figure image img.img-6ab1bb006d9243d2f06f0e938df4eea8llymu500 { width: 774px; height: 507px; }HTML[data-range=”large”] figure image img.img-6ab1bb006d9243d2f06f0e938df4eea8llymu500 { width: 548px; height: 359px; }HTML[data-range=”small”] image figure img.img-6ab1bb006d9243d2f06f0e938df4eea8llymu500, html[data-range=”medium”] figure image img.img-6ab1bb006d9243d2f06f0e938df4eea8llymu500 { width: 564px; height: 369px; }
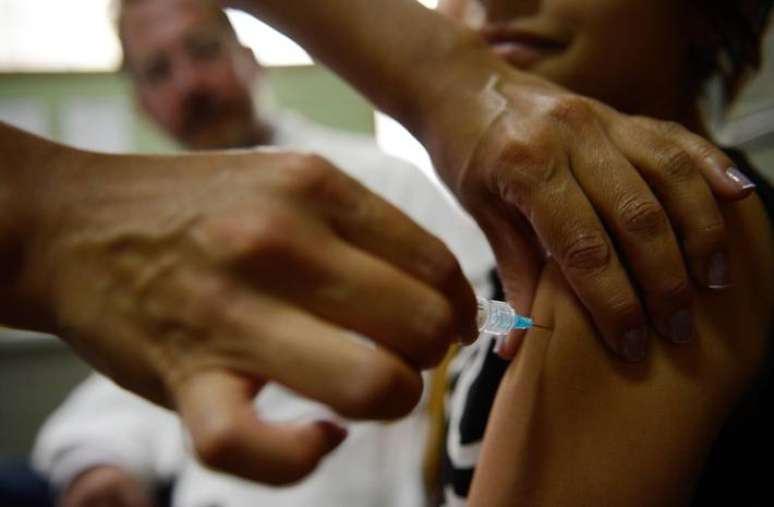
It is important to get vaccinated against HPV
Another decisive element is vaccination, the main form of prevention against HPV. The SUS makes the vaccine available free of charge, which provides protection against high-risk HPV 16 and 18, responsible for most virus-related cancers. Girls and boys between the ages of 9 and 14 can be vaccinated free of charge, as well as people with HIV/AIDS, transplant recipients and immunocompromised people between the ages of 9 and 45.
Zanella recalls the importance of vaccinating especially young people, who have low vaccination coverage in Brazil. “They are the population most susceptible to oropharyngeal cancer caused by HPV, and that’s where the vaccine has the least penetration, due to lack of knowledge or parental forgetfulness,” she warns.
Finally, the combination of HPV infection with other predisposing factors to the disease, such as smoking and alcohol consumption, can increase the risk of developing the disease. “All cancers need an interaction between our body and external factors to manifest themselves. A throat already sore from chronic tobacco abuse and alcohol consumption may become more prone to developing HPV-related cancer “, explains the surgeon of the Santa Casa de Porto Alegre.
Experts still point out that HPV throat cancer has a better prognosis and greater chance of cure than other causes. “It responds much better to treatment than throat cancer caused by cigarettes or alcohol. They look like two completely different diseases, but occurring in the same place and with the same name. They are biologically distinct in terms of their aggressiveness and response to treatment,” he describes Zanella who, in all cases, leaves the alert: “A lesion that doesn’t heal in two weeks or a sore throat that doesn’t go away deserves medical attention”.
Source: Terra
Ben Stock is a lifestyle journalist and author at Gossipify. He writes about topics such as health, wellness, travel, food and home decor. He provides practical advice and inspiration to improve well-being, keeps readers up to date with latest lifestyle news and trends, known for his engaging writing style, in-depth analysis and unique perspectives.

-1jyajqq3d5lya.jpg)




-1hrlykellx8ae.jpg)
