The technique is less invasive, has a faster recovery and a lower risk of complications
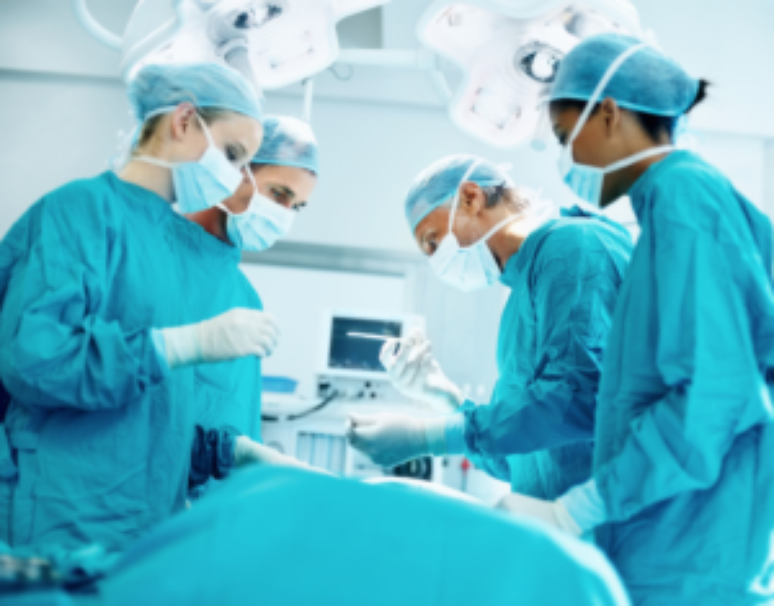
Information from the World Health Organization (WHO) shows that 80% of the world’s population suffers from back pain. The numbers for Brazil are not negligible: 40 million people are affected by the problem, which has disc herniation among the main causes. Approximately 300,000 Brazilians undergo surgery each year to treat a herniated disc. Traditional surgery presents good results in relation to its effectiveness. However, it can cause complications, such as infections, and still require a long rehabilitation period for the patient. The literature also points out that the procedure can affect important structures of the spine, such as muscles and ligaments, damaging them partially or completely, causing pain and even dysfunction.
Procedure
However, a minimally invasive method, still little known in Brazil, avoids all these problems. This is endoscopic spine surgery, which is less aggressive on the body. “It is no longer necessary to make a large incision to access the injured area. Patients are discharged the same day. The risk of postoperative complications and recovery time,” says spine surgeon Dr. Bruno Aprile, of Clinica Sou . Experts point out that Endoscopic Spine Surgery can play an important role in the treatment of herniated discs in adolescents, practitioners of competitive sports and athletes, who need (or want) to have a faster functional recovery. Although it is a minimally invasive procedure, it is necessary to carry out a clinical evaluation and tests before performing the surgery. The doctor must request that the patient fast for eight hours, from liquids and food. In addition, aseptic measures are taken to avoid contagion.
html[data-range=”xlarge”] figure image img.img-38faf5d19d6912884a7c9d8d5e3220db71c7y136 { width: 774px; height: 606px; }HTML[data-range=”large”] figure image img.img-38faf5d19d6912884a7c9d8d5e3220db71c7y136 { width: 548px; height: 429px; }HTML[data-range=”small”] figure figure img.img-38faf5d19d6912884a7c9d8d5e3220db71c7y136, html[data-range=”medium”] figure image img.img-38faf5d19d6912884a7c9d8d5e3220db71c7y136 { width: 564px; height: 442px; }
The benefits
The risk of fibrosis (poor muscle healing) and muscle injuries, which usually cause pain even after full recovery from surgery, becomes minimal. The fact that the muscles around the spine are not cut, but “removed”, causes less trauma to the patient’s body. This way, the risk of bleeding and infection is much lower, as the cuts are smaller than in conventional surgery. The stay in the operating room is much shorter, the scar left is small and the patient can walk a few hours after the operation, being discharged the same day. With a faster recovery, the patient returns to professional and usual activities sooner. Several other diseases can be treated with this technique, which mainly focuses on the release generated by the compression of the nerve, without destroying other structures, and therefore minimizing the need for the use of prostheses, screws or other implants in the spine, as well as the effects resulting from these plants. or blockage (arthrodesis)
slipped disc
A herniated disc results from the wear of the intervertebral discs, whose function is to prevent friction and reduce the impact between the vertebrae. The wear alters the positioning of the disc and causes compression of the nerve roots. The cervical and lumbar regions are most affected due to movement and load bearing. A herniated disc is caused by genetic predisposition, sedentary lifestyle, smoking and aging. The habit of lifting or carrying heavy objects can also lead to herniated discs. In Brazil alone, it affects about 5.4 million people. The diagnosis of herniated disc is made through the clinical examination, but to know the extent of the problem and confirm the affected region, other procedures such as x-rays, MRIs and tomography must be performed.
Source: Terra
Ben Stock is a lifestyle journalist and author at Gossipify. He writes about topics such as health, wellness, travel, food and home decor. He provides practical advice and inspiration to improve well-being, keeps readers up to date with latest lifestyle news and trends, known for his engaging writing style, in-depth analysis and unique perspectives.