The oncologist clarifies the main doubts about melanoma, a neoplasm that represents 3% of skin cancer cases in Brazil
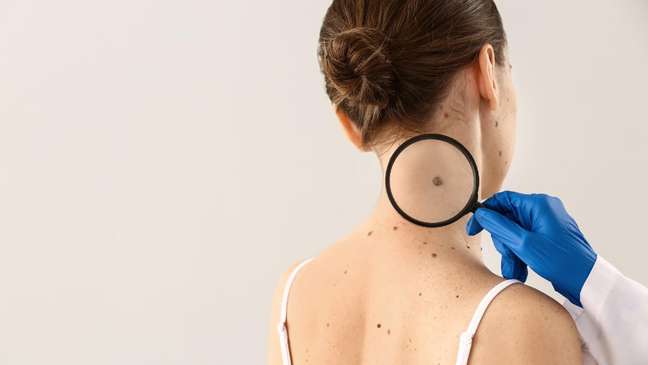
Although rare, melanoma is the most aggressive type of skin cancer, especially if not treated early. According to the National Cancer Institute (Inca), Brazil records more than 185,000 cases of skin cancer annually. Melanoma accounts for 3% of this total.
Given its high ability to metastasize (disease spread to other organs), it is essential to pay attention to the first signs of disease. The main initial manifestation is the appearance of a dark spot with uneven edges.
The oncologist Dr. Sheila Ferreira stresses the importance of analyzing other factors as well. “The mole or mole has a brownish hue and, although it appears more frequently in areas exposed to the sun, it can appear anywhere on the body, including mucous membranes. In black skin, for example, they can commonly appear on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. “, explains.
Emergency and risk factors
As the specialist informs, melanoma originates in the cells that produce melanin (melanocytes), which are responsible for determining the color of the skin. “Due to prolonged exposure to ultraviolet sunlight and also to artificial tanning chambers, cells begin to reproduce uncontrollably. However, the earlier it is diagnosed, the better the chances of treatment success,” warns the oncologist.
The main risk factors for the development of melanoma are:
- Use of tanning beds;
- Light skin and eyes
- Excessive and prolonged exposure to the sun;
- Family or personal history of skin cancer
How to diagnose melanoma early
Investigation of melanoma should begin when dark spots or moles with irregular edges appear, which can increase over time or even cause itching and peeling at the site. “The changes to be evaluated as suspicious are what we call ABCDE: asymmetry, jagged edges, color and diameter and evolution,” explains Dr. Sheila.
- Asymmetry: when half of the lesion is different from the other side.
- Edges: If the blemish, mole, or blemish has an uneven outline.
- Color: When the lesion has different colors, it can be between red, brown and black.
- Diameter: if the lesion has a diameter greater than 6 mm.
- Evolution: changes in the characteristics of the lesion over time (size, shape, color).
Early diagnosis of melanoma skin cancer can be done by clinical, endoscopic, or radiological examinations. “Through early identification, the chances of a cure can reach 90%. Although the spots or spots are not always skin cancers, it is essential to seek a specialist for the correct diagnosis,” comments the oncologist.
“Bringing information on the subject is essential so that more and more people know the signs of their body and are able to identify any skin abnormalities,” say the media. The specialist also emphasizes the importance of the daily use of sunscreen.
“The good news is that we currently have several treatment options and that the chances of cure greatly increase when the diagnosis is made in the early stages, hence the importance of seeking medical attention early in identifying a suspected lesion.” he points out.
stages of melanoma
According to the oncologist, it is essential to analyze the extent of the neoplasm after diagnosis. “Melanoma skin cancer can be classified into stages (I to IV), with I being the first and IV when there is distant organ involvement, which we call metastasis,” explains Dr. Sheila.
In a simplified way, in stages I and II the thickness of the tumor is variable and, in this case, there is no involvement of the lymph nodes or other organs. In stage III, in addition to the skin, melanoma cells are found in the lymph nodes, but not in other organs. And in stage IV, finally, there is the involvement of other distant organs (such as the lung, liver and brain).
To define the treatment, in addition to staging, the oncologist must also evaluate factors such as symptoms, general condition of the patient, presence of other concomitant diseases, laboratory tests and localization of the tumor, among others.
Treatment
When the disease is diagnosed in the early stages, the only treatment needed is surgery. In cases of locally advanced disease, when there is involvement of the lymph nodes and lymph nodes, some form of complementary treatment may be required to reduce the possibility of the disease returning in the future.
For the more advanced stages, targeted therapy or immunotherapy is the treatment of choice, as they will act on all cells, regardless of location. “However, it is worth remembering that every case is a case and, currently, we have several treatment options. The careful and individualized evaluation done by the oncologist who follows the patient is necessary to determine the best therapy for each person,” says the oncologist.
It is possible to prevent
The expert points out that the best way to prevent melanoma skin cancer is to avoid sun exposure from 10:00 to 16:00, when the rays are at their most intense. “Another way to avoid the situation is to look for shady places, invest in sunscreen, wear UV protective clothing, hats, sunglasses and a suitable lip balm,” guides Sheila Ferreira.
The oncologist also reiterates that the use of sunscreen should also be done on cloudy days, about 15 minutes before leaving the house. “It is important that the sunscreen has at least SPF 30. Reapply every two hours or even after swimming or sweating,” he says.
Dr. Sheila concludes by emphasizing the importance of avoiding artificial tanning beds. “It is worth remembering that they have been banned in Brazil by Anvisa (National Health Surveillance Agency) since 2009,” she concludes.
Source: Dr. Sheila Ferreira, oncologist.
Source: Terra
Benjamin Smith is a fashion journalist and author at Gossipify, known for his coverage of the latest fashion trends and industry insights. He writes about clothing, shoes, accessories, and runway shows, providing in-depth analysis and unique perspectives. He’s respected for his ability to spot emerging designers and trends, and for providing practical fashion advice to readers.






-t4ibkqt14qpk.jpg)
