The bronchi, structures affected by the disease, have the task of transporting air to the pulmonary alveoli. Find out more!
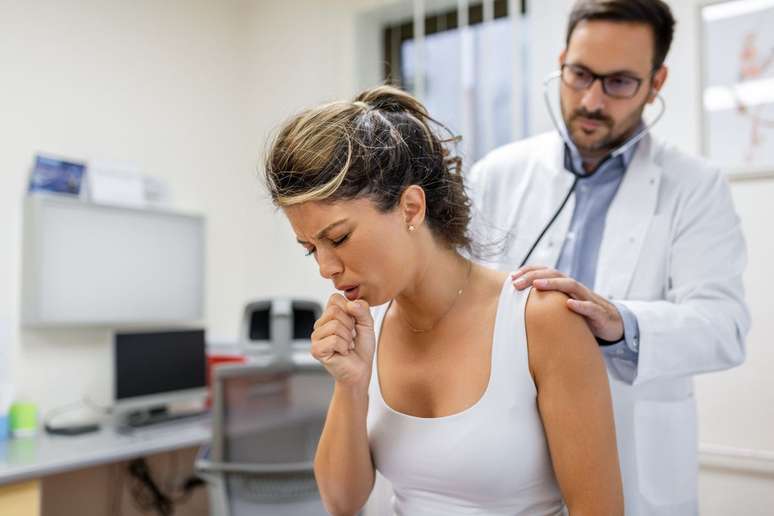
A bronchitis It is an inflammation of the bronchi, structures responsible for transporting air to the pulmonary alveoli, where gas exchange takes place.
“It is one of the most common respiratory diseases and, among its types, the acute form is one of the main causes of medical demand, affecting the health of children and adults. In autumn and winter it is common to observe an increase in cases, since there is a direct relationship with climatic conditions”, explains the Dr. Karina Pierantozzi Verganipediatric pulmonologist and professor of Medicine at the Universidade Cidade de São Paulo (UNICID).
What is the difference between acute and chronic bronchitis?
Bronchitis can be classified as acute OR newsdepending on the duration and frequency of symptoms, according to the Dr. Michelle Andreatapulmonologist at Health at homecompany specializing in home care.
In general, the acute bronchitis occurs in response to a respiratory infection and causes flu-like symptoms and cough that may be dry or productive. It’s a temporary framework lasting a few days or weeks.
“Most of the time it is caused by a infectious agent (virus or bacteria) which generates a direct irritant effect on the tracheobronchial mucosa, triggering a local inflammatory process and an increase in mucus production”, says Dr. Karina.
Already the chronic bronchitis is characterized by the presence of a productive cough – i.e. with sputum – for most days of the month, for three months a year, for at least two consecutive years, states the Dr. Maria Alenitapulmonologist and coordinator of the Medicine course at the João Pessoa University Center (UNIPÊ).
Often, the second type is associated with smoking habit and respiratory conditions such as asthma AND chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
What are the symptoms of bronchitis?
According to doctors, the symptoms of bronchitis I am:
- Dry or productive cough;
- Shortness of breath;
- Wheezing in the chest;
- Fatigue;
- Mild fever;
- Chest pain or cough or deep breathing.
“Usually, acute bronchitis is a consequence of a viral infection. Therefore, the patient may present with upper airway symptoms, such as a runny nose,” adds Dr. Maria.
“Unlike pneumonia, acute bronchitis, in most cases, is not accompanied by high fever and increased heart and respiratory rate,” emphasizes Dr. Karina.
What causes bronchitis?
To the viral respiratory infections are the main causes of acute bronchitis, with bacterial are responsible for fewer cases.
OR to smoke, both active and passive, represents the main risk factor for the development of chronic bronchitis. “Bronchiectasis (structural changes of the bronchi) may be related to the chronic form of the disease, especially in patients suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD),” says the UNICID professor.
Air pollution, dust AND exposure to chemicals AND irritating agents they also contribute to the problem. “It is essential to underline that closed and crowded places increase the possibility of viral and bacterial contamination, favoring bronchitis”, explains Vergani.
How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis of bronchitis involves the patient history and the physical exam. When necessary, especially in chronic bronchitis, chest x-rays, sputum tests, and spirometry (lung function tests) may be requested, which help evaluate the presence of airway obstruction.
And the treatment?
OR treatment of bronchitis acute treatment aims to relieve symptoms and, in addition to including rest, hydration and the use of air humidifiers, decongestants, bronchodilators, cough suppressants and medicines to reduce the sensation of discomfort may be indicated.
“Antibiotics are usually not recommended unless a bacterial infection is suspected,” reveals Andreata.
“For chronic bronchitis, the focus is reduce exposure to risk factors, such as smoking, and manage symptoms. This may depend on bronchodilators, to reduce airway obstruction, inhaled corticosteroids, vaccines to prevent respiratory infections and, in serious conditions, oxygen therapy or pulmonary rehabilitation programmes”, underlines the pulmonologist from Saúde no Lar .
Measures such as getting vaccinated, avoiding addictions, eating well, exercising, washing your hands regularly and drinking plenty of water are essential to prevent bronchitis.
Source: Terra
Ben Stock is a lifestyle journalist and author at Gossipify. He writes about topics such as health, wellness, travel, food and home decor. He provides practical advice and inspiration to improve well-being, keeps readers up to date with latest lifestyle news and trends, known for his engaging writing style, in-depth analysis and unique perspectives.



-sl6oy2p06omu.png)



![Such a great sun in advance: Elizabeth’s Terrible Accidental Victims … which Waiting for You Week until August 25, 2025 [SPOILERS] Such a great sun in advance: Elizabeth’s Terrible Accidental Victims … which Waiting for You Week until August 25, 2025 [SPOILERS]](https://fr.web.img6.acsta.net/img/d0/c4/d0c4d9256b5997c98008a65d7a43177e.jpg)
