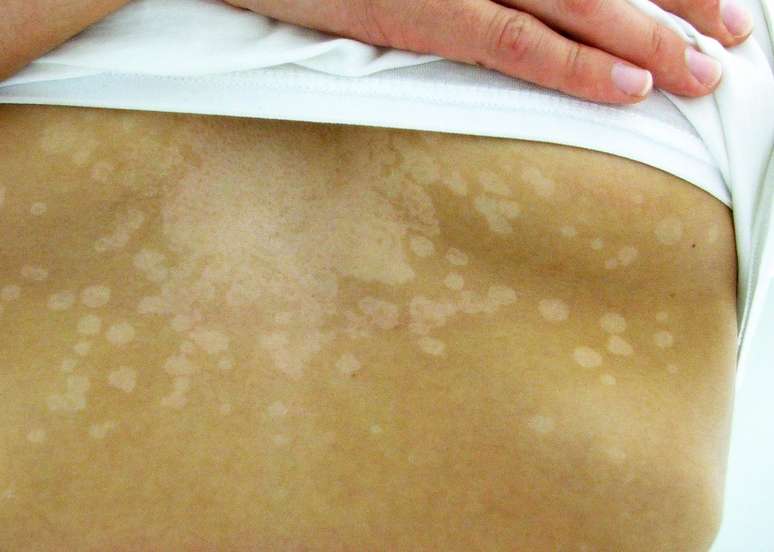
The condition is known by three names and is the result of a fungus
What is white cloth on skin?
The official name is Pityriasis Versicolor but it is also known as white cloth or beach mycosis. The condition is caused by a fungus.
The Malassezia fungus is a type of yeast that is commonly found on the surface of the skin and does not typically cause health problems: in fact, many microbiota (or microscopic organisms), including yeasts like Malassezia, that live in large communities on the skin help to protect it from infections and other pathogens that can cause damage or disease.
Sometimes, however, this fungus can grow out of control and affect the natural color or pigmentation of the skin. When this happens, you may develop patches of skin that are lighter than the surrounding skin.
This condition is not contagious.
What causes white cloth on skin?
Doctors aren’t sure why the fungus can grow out of control, but certain factors can lead to this growth, including:
- hot and humid climate;
- excessive sweating;
- oily skin;
- a weakened immune system;
- hormonal changes.
Pityriasis versicolor can occur in people of all ethnicities and is most common in adolescents and young adults. Adults are more likely to develop the condition if they visit an area with a subtropical climate.
What are the symptoms of white cloth on the skin?
Discolored skin patches are the most noticeable symptom and usually appear on the arms, chest, neck or back. These points can be:
- light (most common) or darker than surrounding skin;
- pink, red, beige or brown;
- dry, itchy and scaly;
- prone to disappear in colder and less humid climates
White cloth on the skin and similar conditions
- Vitiligo
Some conditions with overlapping symptoms, such as vitiligo, are often confused with Pityriasis Versicolor. However, vitiligo can differ in several visible ways, as vitiligo does not affect the structure of the skin, often appears on the fingers, wrists, armpits, mouth, eyes or groin, and often forms symmetrical patches.
- Pityriasis rosea
The rash caused by pityriasis rosea also looks like white cloth, but is usually preceded by a solitary red patch of scaly skin that appears a few days or weeks before the rash. This rash often appears in the form of a Christmas tree on the back. It is not known what causes this condition. But, like pityriasis versicolor, it is neither harmful nor contagious.
What are the risk factors for developing white tissue on the skin?
Several environmental and biological factors can increase the risk of this condition, including:
- family history;
- excessive sweating;
- a humid and hot climate;
- a weak immune system;
- taking drugs that weaken the immune system;
- some types of cancer.
When should you contact your doctor?
You may choose to treat the condition yourself. Over-the-counter (OTC) antifungal medications can clear up discolored skin patches. However, you should contact your doctor if these treatments are not effective, as you may need a prescription medication to control your symptoms.
How long will it take for your skin to return to normal?
Even after clearing the infection, your skin may remain discolored for several weeks or months after treatment. The infection can also return when the weather becomes warmer and more humid. If your condition returns, your doctor may prescribe medications once or twice a month to prevent symptoms.
Source: Terra
Ben Stock is a lifestyle journalist and author at Gossipify. He writes about topics such as health, wellness, travel, food and home decor. He provides practical advice and inspiration to improve well-being, keeps readers up to date with latest lifestyle news and trends, known for his engaging writing style, in-depth analysis and unique perspectives.