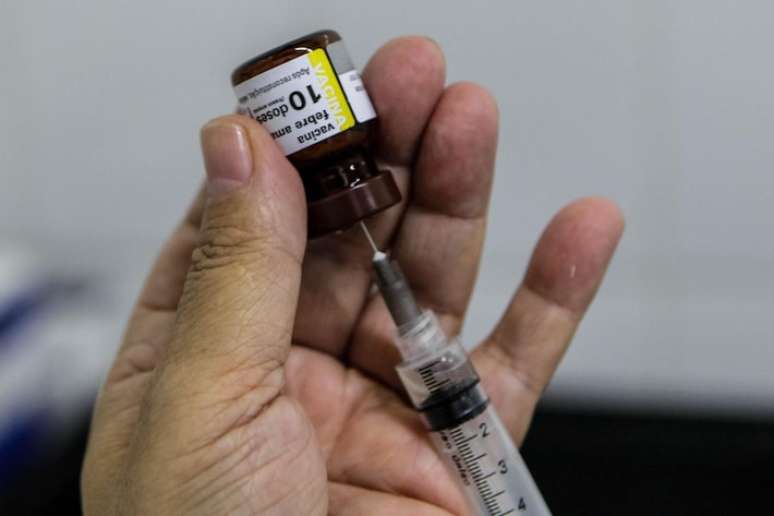
The patient is a 21-year-old man who has not been vaccinated against the disease; the vaccine is available at health centers
The Department of Health of the State of São Paulo (SES-SP) recorded this Friday the 17th a new human case of yellow fever. It is the second confirmed this week.
The patient is a 21-year-old young man, resident in Santo André, who recently traveled to Joanópolis, in the hinterland of São Paulo. The ministry did not communicate the boy’s health status.
On Monday 13th the secretariat reported the first case of 2025. At the time, the SES reported that the patient was a 27-year-old man, resident in the capital São Paulo, who had lived in a rural area in the municipality of Socorro, also in the Campinas region.
In both cases the men did not take the vaccine, the main protective measure against complications of the disease.
Until then, the last cases in the state had been recorded in the first half of 2024. In March, a 50-year-old man who lived in Águas de Lindóia and traveled to the Monte Sião region of Minas Gerais died. due to illness. Shortly afterwards, in the rural area of Serra Negra, a 28-year-old boy was diagnosed with the disease. He was vaccinated and recovered completely.
Deaths of monkeys
Four howler monkeys were found dead in the forest on the campus of University of Sao Paulo (USP) In Ribeirao Preto, the week between Christmas and New Year. Tests confirmed that the animals were victims of yellow fever.
Furthermore, tests confirmed five other cases in non-human primates: one in Pinhalzinho, in the Campinas region; three in Ribeirão and one in Socorro.
In light of the confirmations, the SES has expanded the team training actions in the municipalities with particular attention to vaccination, vector control and treatment of suspected cases of the disease. According to the ministry, 55 thousand vaccine doses were sent to Ribeirão Preto and 75 thousand to the Campinas region.
How does the transmission happen?
There are two different cycles of yellow fever transmission, wild and urban. In the wild cycle, monkeys are the main hosts and the vectors are mosquitoes of the genera Emagagogue AND Sabete. Man participates in this cycle as an accidental guest when he visits forest areas. In the urban cycle, humans are the only host with epidemiological relevance and transmission occurs through mosquitoes Aedes aegizi infected.
Can yellow fever be transmitted by monkeys?
No. Although monkeys host the disease in its natural cycle, it is only transmitted by infected mosquitoes.
What is the best way to protect yourself?
The main protective measure against yellow fever is vaccination. Currently the vaccination program includes one dose of vaccine at 9 months of age and another at 4 years of age. In people over 5 years of age who have not previously been vaccinated, the single-dose scheme is used. The vaccine is offered free of charge in health centers across the country.
What are the symptoms of yellow fever?
According to the Ministry of Health, the initial symptoms of the disease are: sudden fever, chills, pain in the head, back and body in general, as well as nausea, vomiting and weakness.
Typically, people improve after these symptoms, but 15% remain symptom-free for about a day and then progress to more severe conditions. Therefore, it is important to have medical monitoring.
Source: Terra
Ben Stock is a lifestyle journalist and author at Gossipify. He writes about topics such as health, wellness, travel, food and home decor. He provides practical advice and inspiration to improve well-being, keeps readers up to date with latest lifestyle news and trends, known for his engaging writing style, in-depth analysis and unique perspectives.


-to2c6pqzbwaf.png)



