Essential for environmental balance, bees pollinate plants and maintain biodiversity. Find out how many species exist in the world
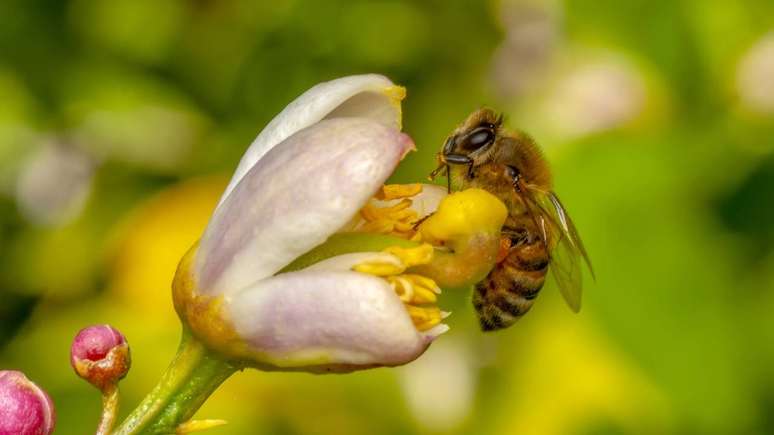
Present on practically all continents, bees represent one of the main pollinators on the planet. The role of these insects goes far beyond honey production, directly influencing the biodiversity and survival of various plant and animal species. The role of bees, fundamental for ecological balance, arouses the interest of scholars, environmentalists and society in general.
Many agricultural crops depend on bees for fruits, seeds and other products essential for human and animal nutrition. This process, called pollination, contributes to the development of wild and agricultural plants, making bees the protagonists when thinking about maintaining ecosystems and guaranteeing global food security.
Why are bees so important for the environment?
Pollination by bees accounts for approximately 75% of global food crops. Without the work of these insects, many foods would encounter strong barriers to their development. Furthermore, the genetic variety of plants is highly dependent on this service, which makes the environment more resilient.
- Increase in agricultural productivity: Bee-pollinated crops have higher yields and quality.
- Conservation of native flora: Many plant species depend exclusively on bees to reproduce.
- Support for food chains: Small animals and birds consume fruits and seeds that exist only through pollination.
The presence of bees strengthens the healthiness of natural environments and urban areas. They also play a role in the production of natural products, such as honey and propolis, which are part of diets and medicinal systems in several cultures around the world.
How many species of bees exist today?
According to recent studies, it has been identified that there are approximately 20 thousand species of bees distributed globally. This diversity ranges from specimens of a few millimeters to species of considerable size, adapted to different climates and regions.
- Stingless Bees (Meliponine): Widely present in tropical areas, especially in South and Central America, they play an important role in the pollination of forests and plantations.
- Social Bees: Like the popular Apis melliferawhich forms colonies with well-defined functions including workers, queens and drones.
- Solitary bees: Responsible for the pollination of wild plants of agroecological importance, despite being less known and observed.
The identification of new species occurs continuously thanks to scientific research, which mainly investigates little-explored regions. The real number of bee types could be even greater, considering that many specimens have not yet been formally described by science.
What impact does bee protection have on society?
The attention paid to bee conservation has a direct impact on crop stability, access to fresh and healthy food and the maintenance of ecosystem services. Without these pollinators, both small and large farming communities would suffer significant losses.
- Reduction in the availability of fruit and vegetables in open-air markets and supermarkets;
- Increase in food prices due to reduced supply;
- Environmental imbalance, with impacts on other species of plants and animals;
- Damage to economic chains dependent on honey and other bee products.

Sustainable management initiatives, restoration of natural habitats and reduction of the use of agricultural chemicals are the measures suggested by experts to preserve these essential insects. Raising awareness about the role of bees facilitates the development of public policies and mobilizes different sectors in favor of biodiversity.
Every day the direct link between the health of bees and the future of human societies becomes more evident. By strengthening the defense of these pollinators, not only is the environment protected, but also the basis of modern life and food production.
Source: Terra
Ben Stock is a lifestyle journalist and author at Gossipify. He writes about topics such as health, wellness, travel, food and home decor. He provides practical advice and inspiration to improve well-being, keeps readers up to date with latest lifestyle news and trends, known for his engaging writing style, in-depth analysis and unique perspectives.