Find out what they are for and what types of digital signal processors are found in consumer electronics, including smartphones, headphones and TVs
DSP (Digital Signal Processor) is a microprocessor specialized in handling digital signals, such as audio and video. It is present in electronics that are part of our daily lives, such as cell phones, smart TVs and Bluetooth headphones.
A digital signal processor can execute mathematical algorithms in real time more efficiently. This allows the creation of noise cancellation systems (ANC) and the improvement of image definition (upscaling) with low power consumption. Understand, therefore, the functions of the DSP.
Index
- What is the difference between digital and analog signal?
- What are DAC and ADC converters?
What is a digital signal processor (DSP) used for?
One digital signal processor (DSP) Its main function is to process digital signals on a computer, such as audio and video. It is used to manipulate the signal with specific algorithms, which can improve the clarity of a voice or decrease the noise in an image.
More efficient noise cancellation
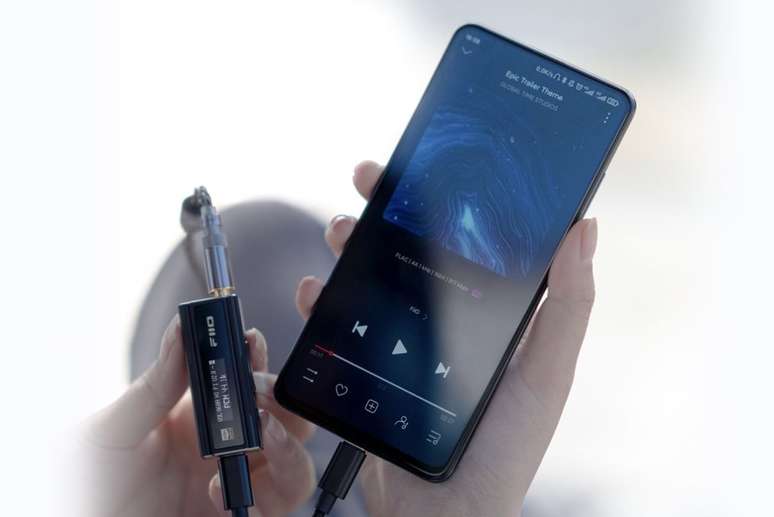
In an active noise canceling (ANC) headphone, the DSP captures ambient sound (noise) through the microphones and creates a reverse sound wave, which is then played back. When noise and the reverse sound wave meet, they cancel each other out, which gives the impression of a quieter environment.
The efficiency of an ANC technology is related to the DSP. A superior chip can identify the differences in the ambient sound and create the reverse sound wave faster. That’s why headphones with ANC work well for constant noise (like motors) but not always for sudden spikes (like conversations).
Color correction, sharpness and other image parameters
DSPs are also effective at improving the quality of a signal through digital filtering algorithms. An image signal processor (ISP), which is a type of digital signal processor, is involved in color balance, sharpness, lens correction, and other factors, enhancing the visual appearance of photos and videos.
In general, DSPs are better than CPUs at signal processing because they are more efficient at performing specific operations, such as loading and accumulating, or multiplying and accumulating, used in digital filters. Even the first chips, released in the 1980s, executed these instructions in nanoseconds (ns).
How does digital signal processing work?
OR digital signal processing it works by manipulating originally analog signals, such as sound and light waves, into a digital format. The technique allows complex mathematical calculations to be applied to enhance, filter or extract information from these signals.
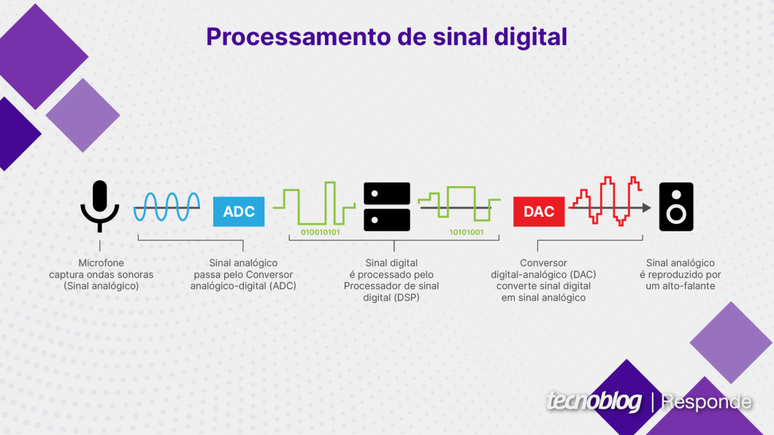
The transformation of the analog to digital signal begins with the acquisition equipment — such as a microphone (for sound waves) or an image sensor (for light waves). This analog signal passes through the analog-to-digital converter (ADC), which transforms the continuous waves into a series of discrete samples, which can be digitally represented, in bits.
DSP comes into play after the analog waves have already been converted into digital signals. It can filter out unwanted noise from an image, adjust specific frequencies of a sound (equalization), and run other types of algorithms. Signal processing can be done in real time or at a later time.
If necessary, the digital signal already processed by the DSP can be converted back to an analog signal using a digital-to-analog converter (DAC). This process occurs when a digital music file needs to be played through a speaker, which reproduces sound waves.
What is the difference between digital and analog signal?
One analog signal it is a continuous form, which can vary infinitely within a range of values. already a digital signal it is represented in binary numbers (0 and 1), i.e. it is a discrete form with a finite amount of values.
Digital signals use a series of mathematical calculations to represent continuous waves in the form of bits. They are important in an electronic context because they are more flexible and robust than an analog signal. For example, a sound wave recorded on a vinyl record can be damaged by dust and scratches.
A continuous wave can lose information when it is converted into a digital signal. A sampling is a technique that measures the value of an analog signal at regular time intervals, creating a series of values that will compose the digital signal. The higher the sampling rate, the higher the frequency of the measurements, which reduces losses.
Also, converting from analog to digital involves the quantization, which is the process of mapping infinite values of continuous waves to a set of finite numbers in a digital representation. Since there are limitations in this process, quantization noise can occur, leading to loss of detail in a music or picture.
What are DAC and ADC converters?
DAC (Digital to Analog Converter) AND ADC (analog to digital converter) they are essential analog to digital signal converters in DSP-equipped electronics, such as speakers, headphones, digital cameras, and smart TVs.
An ADC converter measures the analog signal at regular time intervals and converts it into a binary format. The sampling frequency is the frequency at which measurements are taken and is usually measured in hertz (Hz). The precision of these measurements, also called resolution, is measured in bits. A higher sampling and higher resolution ADC generates a digital signal that is more faithful to the original.
A DAC converter analyzes a series of digital data and transforms it into an analog signal. Since the digital signal is represented by discrete points, an interpolation technique must be used to reconstruct the analog waves. This is done with a low-pass filter, which determines which frequencies will pass when recreating the signal.

What are the types of digital signal processor (DSP)?
We can classify digital signal processors into two groups: fixed-point DSPs and floating-point DSPs. Understand more about them:
- fixed point DSP: processes integers, i.e. is less accurate. It is efficient for handling a large volume of real-time data and is generally cheaper. It can be used in systems where speed is more important than processing accuracy;
- DSP floating point: processes floating point numbers, i.e. is more accurate. It is efficient for handling data that requires high fidelity, such as Hi-Fi audio. It’s generally cheaper, and its real-time performance is less predictable.
Who are the main manufacturers of digital signal processors (DSP)?
- Texas Instruments (TI): founded in 1930, is an American company specializing in DSP for various applications, from audio and video to chips for the industrial segment;
- Analog Devices: American company created in 1965 that produces DSPs for communication equipment, as well as processors for the automotive and medical sectors;
- Qualcomm: Best known for Snapdragon-brand SoCs (System-on-a-Chip) for mobile phones, which contain DSPs for processing audio, video, and radio frequency signals;
- NX extension: Originally created in 1975 in the Netherlands as Philips Semiconductors, it has been an independent company since 2006 and develops DSPs for cars, smartphones and industrial equipment.
What is a digital signal processor (DSP)?
Source: Terra
Rose James is a Gossipify movie and series reviewer known for her in-depth analysis and unique perspective on the latest releases. With a background in film studies, she provides engaging and informative reviews, and keeps readers up to date with industry trends and emerging talents.


![Everything starts here: What awaits you on May 13, 2025, on Tuesday, 1174 episodes of 1374 [SPOILERS] Everything starts here: What awaits you on May 13, 2025, on Tuesday, 1174 episodes of 1374 [SPOILERS]](https://fr.web.img2.acsta.net/img/c5/5c/c55cb027831848dfcf9440f50d04e75b.jpg)




