In places where contamination by microorganisms is present, contact can lead to infections of the mouth, eyes and other mucous membranes.
Summary
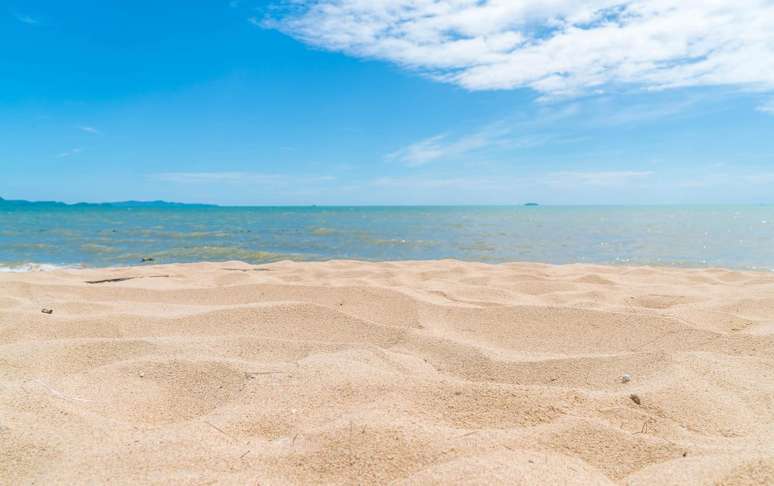
Take care of your health when visiting the beach, for example by avoiding contamination, skin burns and taking care of intimate hygiene.
The end of the year has arrived and, with it, the desire to enjoy the beach. Many are already preparing to go down to the coast and, whether with family or friends, the idea is just to take a chair, an umbrella and enjoy a swim in the sea. A survey by the Ministry of Tourism shows that 51% of Brazilians prefer beaches as a destination for their summer holidays.
However, experts warn: in addition to packing your bags, it is essential to take care of your health during the trip. “Direct contact with sand does not in itself cause disease. The problem is that sand can often be contaminated with microorganisms. If the contamination reaches the mouth, eyes or other mucous membranes, it can cause infections,” explains Larissa Hermann, medical clinic at the Cajuru and São Marcelino Champagnat hospitals.
Microorganisms found in sand include parasites that feed on organic materials in the soil and can carry bacteria into the human body, either through the mouth or through open wounds.
Experts give advice to avoid problems caused by contact with sand.
1. Avoid direct contact with mouth, eyes and open wounds
It is normal for children to play in the sand and put their hands in their mouths or even swallow some sand. “In these cases, the most recommended thing is to observe possible symptoms, such as fever and diarrhea, and contact a doctor if they appear. It is also important to wash your hands often, especially before eating or when touching surfaces after contact with sand,” advises Larissa.
Fungi and bacteria found in sand can also cause contamination through open wounds, leading to infections such as ringworm and woodworm. To avoid this, cover exposed areas well with bandages and maintain good hygiene.
2. Use sunscreen and moisturizer
Prolonged exposure to the sun can cause severe burns and redness, making the use of sunscreen essential. Furthermore, frequent contact with hot sand increases the risk of dry skin and burns.
“Hot sand can remove the natural oil layer from the skin, leaving it dry and more vulnerable to burns. To avoid problems, the ideal is to avoid prolonged direct contact, using towels, sarongs or mats when sitting or lying on the sand. It is essential to apply and reapply sunscreen throughout the day as it provides an additional barrier. The moisturizer, in turn, is essential to prevent dryness caused by rubbing with sand”, underlines Anna Karoline Tomazini, dermatologist at the São Marcelino Champagnat and Universitário Cajuru hospitals.
3. Beware of damp underwear
This tip is especially important for women. Wet bikinis can aggravate genital diseases, such as candidiasis. Heat and excessive sweating already favor the growth of fungi in the vaginal region, and prolonged humidity creates an ideal environment for the development of microorganisms, especially when sand accumulates after swimming in the sea or when sitting directly on the sand .
“The vagina already naturally contains bacteria and fungi, but a significant increase in these microorganisms can trigger genital diseases. To avoid problems, it is important not to sit directly on the sand, avoid wearing wet swimsuits for a long time and, when possible, change and shower with plain water. It is also essential to reduce heat and humidity in the intimate area,” advises Renata Hayashi, gynecologist at the Women’s Health program at the São Marcelino Champagnat hospital.
4. Get cleaning supplies
In addition to bacteria and fungi, fine sand can cause problems when it comes into contact with the eyes, causing irritation and even lesions due to scratching and itching. “Grains of sand have rough surfaces that can scratch the cornea, the clear outer layer of the eye. These scratches can cause intense pain, redness, excessive tearing and photophobia, i.e. sensitivity to light,” explains Dhiogo Corrêa, ophthalmologist at the São Marcelino Champagnat and Universitário Cajuru hospitals.
To avoid complications, it is recommended to bring lubricating eye drops, saline solution and a bottle of clean water to the beach. These items make it easier to clean your eyes and help prevent more serious injuries or irritation.
inspires transformation in the world of work, in business, in society. Compasso, a content and connection agency, is born.
Source: Terra
Ben Stock is a lifestyle journalist and author at Gossipify. He writes about topics such as health, wellness, travel, food and home decor. He provides practical advice and inspiration to improve well-being, keeps readers up to date with latest lifestyle news and trends, known for his engaging writing style, in-depth analysis and unique perspectives.






-t4ncqljsx55w.jpg)
